WASHINGTON — The European Space Agency will seek funding this fall for a feasibility study of space-based solar power, the latest sign of support for a concept that still faces significant technical and financial challenges.
Josef Aschbacher, the director general of ESA, tweeted on August 16 that he will ask member states at this November’s ministerial meeting to finance a preparatory program for space-based solar power (SBSP) called Solaris. He did not disclose how much funding he was asking for Solaris.
“We have the main building blocks already, but let me be clear: for the project to succeed, a lot of technology development and funding is still needed,” he wrote.
Solaris, according to ESA, will be a three-year study to address technical issues associated with SBSP, a concept where solar energy is converted into electricity and then transmitted to Earth for terrestrial use. The study examines potential business opportunities for SBSP development and addresses policy issues.
“It ensures that Europe becomes a key player – and potentially a leader – in the international race towards scalable clean energy solutions for climate change mitigation,” ESA says on a web page about Solaris. The three-year study would support a decision at the next ministerial meeting in 2025 on proceeding with a full SBSP development effort.
ESA is seeking funding for Solaris following two independent cost-benefit studies by consultancy firms Frazer-Nash in the UK and Roland Berger in Germany. Both concluded that the SBSP has the potential to meet European energy needs while supporting the “net zero” emissions target by 2050 set by the European Commission
The Frazer-Nash study estimated that the net present value of a European SBSP system from 2022 to 2070 will range between 149 billion and 262 billion euros ($150–264 billion). A central case of 54 “gigawatt class” SBSP satellites would produce 601 billion euros in benefits in that period, primarily from avoided costs of terrestrial energy production together with its carbon dioxide emissions, with 418 billion euros in costs for the development and operation of the SBSP. system.
Roland Berger’s study concluded that one SBSP satellite, based on an existing design, could cost at least 8.1 billion euros to build and 7.5 billion euros to operate for 30 years, assuming “substantial advances” in key technologies. In the worst case scenario without those advances, the same design would cost 33.4 billion euros to build and 31.1 billion euros to operate. Despite the uncertainty, concluded SBSP “has strong potential to become a competitive renewable technology.”
The ESA initiative comes amid a resurgence of interest globally in SBSP, which first had its heyday half a century ago and has periodically resurfaced since then. The UK government has shown interest in SBSP, among other alternative energy technologies it was considering last year.
The China Academy of Space Technology announced in June that it will test wireless power transmission, an essential technology for the SBSP, in low Earth orbit in 2028 followed by a megawatt-class experimental satellite into geostationary orbit by 2030. Those tests are part of a long-term effort that could lead to satellites producing two gigawatts of power in GEO by 2050.
NASA’s Office of Technology, Policy and Strategy announced at the International Space Development Conference (ISDC) in May that it was conducting a short-term study of SBSP, updating existing concepts to reflect the -advances in technology and reduction in launch costs. The agency expects the study to be completed in time to present at the International Astronautical Congress in Paris in September.
SBSP advocates say the potential for major reductions in launch costs enabled by systems like SpaceX’s Starship, combined with the growing demand for clean energy sources to meet net-zero goals , is driving the renewed interest in SBSP by governments. However, even those advocates acknowledge SBSP faces major hurdles, from the economics of such systems to the development of core technologies needed to assemble and operate massive satellites, as well as policy implications associated with beam power from -space.
The deployment occurs in two stages: the first part occurs about five minutes after the separation and is driven by the spring, deploying the solar arrays to about 40% within four minutes. The second part is motorized, and will fully extend the solar arrays. This part takes about ten minutes.
Do solar panels work better in space?

At 22,000 miles above Earth, the sun is much brighter, so space-based solar panels can collect much more solar energy. They would deliver up to 40 times the annual amount of reliable energy 24/7 that the same cell generates on Earth.
Are solar panels more space efficient? Space-based solar panels can generate 2,000 gigawatts of energy continuously. This is 40 times more energy than a solar panel generates on Earth every year. See the article : San diego diy solar. This is also several times higher than the efficiency of solar panels today.
What advantages do solar cells have in space?
| Advantages of Solar Energy | Disadvantages of Solar Energy |
|---|---|
| Renewable Energy Source | Cost |
| Reduces Electricity Bills | Weather Dependent |
| Various Applications | Solar Energy Storage is expensive |
| Low Maintenance Costs | Uses A Lot Of Space |
What do solar cells do in space?
Solar arrays that convert energy to electricity on the space station are made of thousands of solar cells. Solar cells are made from purified pieces of the element silicon. This may interest you : San diego metropolitan credit union solar loan. These cells directly convert light to electricity through a process called photovoltaics.
What are some of the advantages of using solar cells in outer space?
A space-based solar power station in orbit is illuminated by the Sun 24 hours a day and can therefore generate electricity continuously. This represents an advantage over terrestrial solar energy systems (systems on Earth), which can only produce electricity during the day and depend on the weather.
Do solar cells work better in space?
Solar cells that are made of gallium arsenide are much more efficient, and as a result, are sometimes a better choice when physical space is a concern. These panels can reach up to about 34% efficiency vs.
How do solar panels work in space?
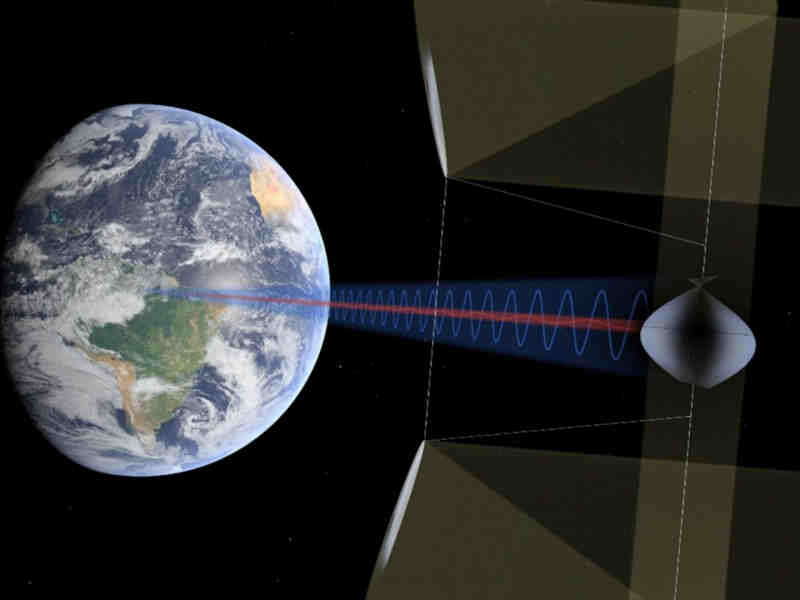
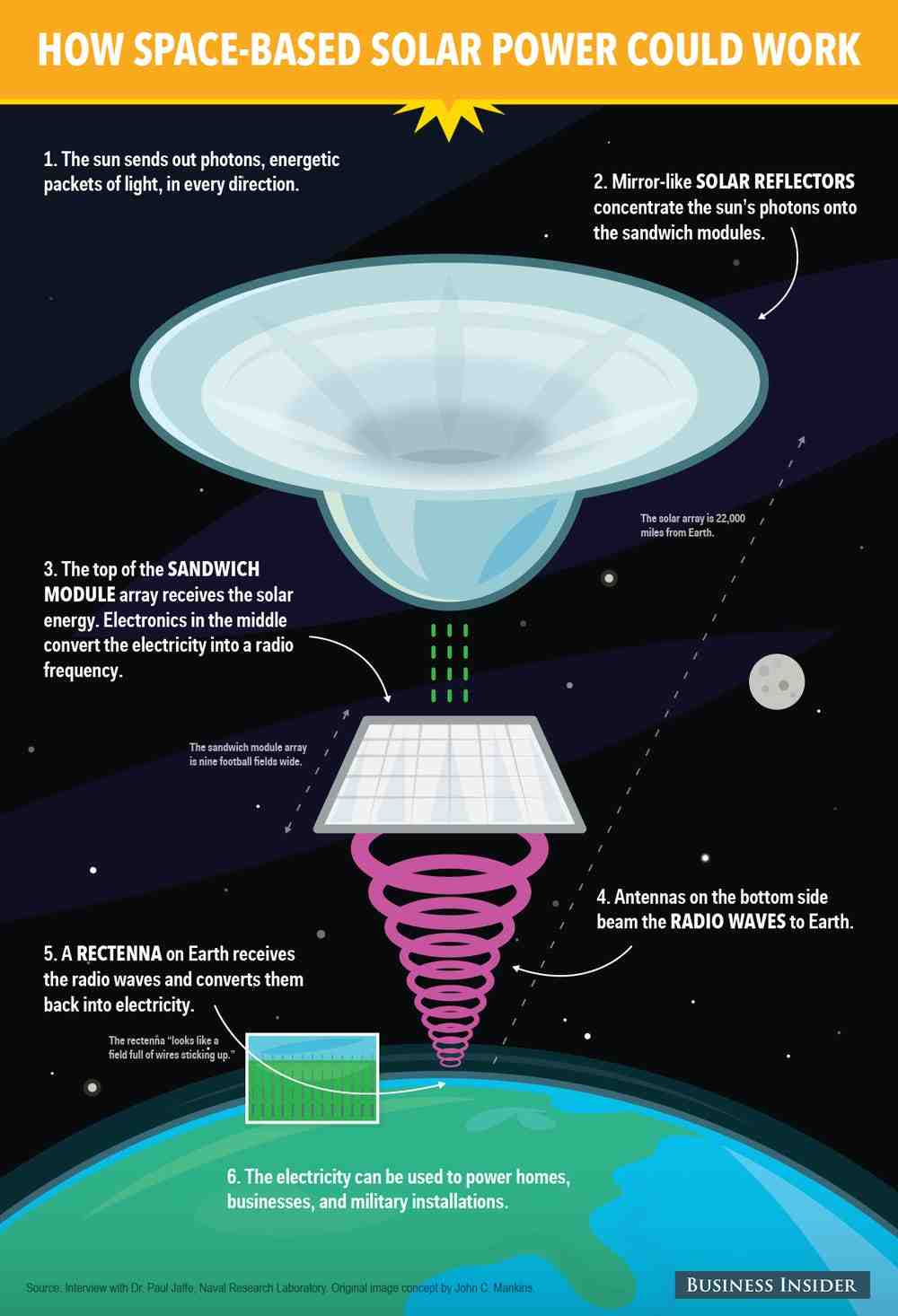
Equipped with solar panels, energy-transmitting satellites collect high-intensity, uninterrupted solar radiation by using giant mirrors to reflect large amounts of solar rays onto smaller solar collectors. This radiation is then transmitted wirelessly to Earth in a safe and controlled manner either as a microwave or laser beam.
Can solar energy be used in space?
Space-based solar power is considered technically feasible primarily due to advances in key technologies, including lightweight solar cells, wireless power transmission and space robotics. Importantly, assembling even a space-based solar power station will require many space shuttle launches.
Why don’t we put solar panels in space?
The environment in space also has various hazards that can cause damage to solar panels. These include space debris and extreme solar radiation, which can degrade solar panels up to 8 times faster than panels installed on Earth.
Would solar power work on Mars?
There is a history of using solar energy on Mars – with the exception of Curiosity (which uses a radioisotopic thermoelectric generator) all Mars rovers rely on solar energy for operations on Mars. But ultimately solar power will be inappropriate for anything much larger than a rover for a number of reasons.
Why is solar energy good on Mars? The use of solar energy limits the places on Mars that the landed rover missions can explore. They are restricted to land and travel around the equatorial region where they can get enough sunlight to re-energize their batteries.
How much power do solar panels produce on Mars?
In Mars, the two panels together produce 1,000 watts of energy. The solar panels were deployed shortly after launch and will remain deployed throughout the mission. (See the cruise configuration as well.) During aerobraking, the solar panels had a special role to play.
Does Mars get enough sunlight to use solar power?
The huge solar arrays provide the station’s electrical power. On Mars the sunlight is strong enough to use solar panels.
How efficient is solar power on Mars?
NASA’s InSight lander generated 4,588 watt-hours during sol 1, a new record for electricity generation on Mars.
How effective is solar energy on Mars?
During the main missions of the rovers, their solar arrays were able to produce about 900 watt-hours of energy for each martian day, or sol. In the well-expanded mission, efforts to strategically move Spirit and Opportunity to and from sun-rich areas are providing up to 410 watt-hours per martian sol.
How efficient are solar panels on Mars compared to Earth?
The maximum solar irradiance on Mars is about 590 W/m2 compared to about 1000 W/m2 at the Earth’s surface. The intensity of the Sun on a horizontal patch of the Earth’s surface of 590W/m2 occurs when the Sun is just 36 degrees above the horizon.
What happens when power goes out and you have solar panels?

If you have solar panels installed on your roof or property they will continue to generate electricity during a power outage, as they do every day because the panels are still absorbing sunlight and solar energy.
How can I use my solar during a power outage? How can you use solar energy to survive a power outage?
- Use a backup gas generator.
- Add solar batteries to your system.
- Use a solar powered generator.
- Replace your inverter with a Sunny Boy or Enphase Ensemble system.
Do you need a backup generator if you have solar panels?
Key takeaways. Solar panels don’t work during a power outage, so homeowners need a backup power supply if they want to run their home without the utility. Gas generators are the most popular form of backup power and can be installed in a home that has solar panels.
Do I need a generator if I have solar?
You may need a generator if you have solar panels to avoid running out of power in the event of an outage (if you have a grid-tied system). Or if you can’t get solar power due to weather or system failure (with an off-grid system) and if you run out of battery power. But, not everything.
Can you use solar power as backup?
Solar powered battery back-up systems for grid power outages are a great alternative to fossil fuel generators. Battery back-up solar PV systems work like regular generator systems, except they also have the added benefit of powering your home with clean, renewable energy during the day.
Can you have solar and a generator?
Unfortunately, you cannot run your home on both solar and generator power at the same time. In other words, the generator and the solar panels cannot operate parallel to each other. As we said before, solar panels send feedback to the grid, creating a dangerous scenario for utility repair workers.
Will solar work if grid goes down?
When disaster strikes, alternative energy sources like solar can keep your power on even when the grid goes down. However, solar panels alone are not enough: you need backup battery storage to stay powered through an outage.
Do solar panels work when the grid is down?
The inverter goes to a smart meter that records the amount of energy you use, and also the excess solar energy that is sent back to the utility. So if the grid goes out, so do your solar panels.
What would happen if the solar grid shut down?
What if the power grid shuts down? If the power grid goes down, water and natural gas will likely fail at some point as well, so planning is critical. Without a plan in place, most of us would be in bad shape with an extended grid outage.
Why don t solar panels work in a blackout?
When the power is turned off by your electric company due to a natural disaster, overload, or even just routine maintenance, your panels will also stop producing power. This is for the safety of utility workers fixing the lines. And yes, that means solar panels alone won’t work during a power outage.
How many types of solar arrays that are used in satellites?
Gimbals are used to rotate the arrays to face the sun to provide maximum power to the space station. Each of the eight solar arrays is 112 feet long by 39 feet wide. The space station’s solar arrays have been installed on several space shuttle missions.
How many types of solar arrays are used in Mcq satellites? Explanation: There are two types of solar arrays that are used in satellites. Those are cylindrical solar arrays and rectangular solar arrays or solar sails.
How many solar panels are on a satellite?
A satellite can have a single solar panel or multiple panels, depending on the energy requirement and the dimensions of the satellite. All the solar panels combined, including the deployment mechanisms to deploy them in orbit, are often referred to as the ‘solar array’ subsystem.
How much do solar panels cost on a satellite?
Typical communications satellite solar panels have a mass per kilowatt of about 20 kilograms, so at current launch costs of $10,000 per kilogram, that comes to $200 per watt – 100 times too high to be competitive at utility level.
Do satellites have solar panels?
Earth-orbiting spacecraft, called satellites, are close enough to the Sun that they can often use solar energy. These spacecraft have solar panels that convert the Sun’s energy into electricity that powers the spacecraft. Electricity from the solar panels charges a battery in the spacecraft.
What solar panels are on satellites?
There are two types of solar cells that are common in spacecraft: Silicon cells coated with thin glass, and. Multi-junction cells made of gallium arsenide and other similar materials.
How many types of solar are there?
The 4 Main Types of Solar Panels There are 4 main types of solar panels available on the market today: monocrystalline panels, polycrystalline, PERC, and thin panels.
What are the 3 types of solar panels?
In this blog we will explore the three main types of solar panel cells: polycrystalline, monocrystalline and thin-film. Understanding the difference between the three, is the first step to choosing your perfect panel for your home, business or community.
What are the 2 types of solar energy systems?
There are two main types of solar energy technologies: photovoltaic (PV) and concentrating solar-thermal energy (CSP).


