Is energy recycled in the biosphere?
The movement of nutrients through the biosphere is different from energy transfer in that, while energy flows through the biosphere and cannot be reused, elements are recycled. To see also : Ice industry in the midst of federal investigation, delays.
What is recycled in the biosphere? Carbon atoms (and all atoms) are used and recycled. They are used by different organisms immediately and are sometimes left on Earth to be used again in millions of years.
What happens to energy in the biosphere?
Flow of Energy in the Biosphere Through photosynthesis, plants convert inorganic inputs (carbon, water, nitrogen, phosphorus, etc. See the article : Efficiency limits of next-generation hybrid photovoltaic-thermal solar technology.) into the millions of different energy-rich organic materials that comprise all organisms.
Does energy get recycled in the biosphere?
Is energy recycled in the biosphere? As noted above, energy cannot be recycled, and is not recycled in an ecosystem. Instead, it flows in and out of the ecosystem.
Does energy get recycled?
Energy is not recycled in ecosystems and every ecosystem requires a sustainable input of energy to sustain it. There is some energy that is converted at each level of the food chain or food web in an ecosystem.
Is energy lost in the biosphere?
Photosynthesis and Solar Energy At the same time, there is a never-ending loss of energy from the Earth. Energy is lost as heat as it radiates back from the earth’s surface, beyond the earth’s atmosphere. Earth’s atmosphere is able to trap some of the heat, warm the atmosphere and make the Earth habitable.
Is energy recycled in an ecosystem?
Energy is not recycled in ecosystems and every ecosystem requires a sustainable input of energy to sustain it. There is some energy that is converted at each level of the food chain or food web in an ecosystem. In an ecosystem, energy often changes from one form to another.
What Cannot be recycled in an ecosystem?
So, the correct answer is ‘Energy.
What happens to energy in an ecosystem?
The biggest source of energy for an ecosystem is the sun. Energy that is not used in the ecosystem is eventually lost as heat. Energy and nutrients are circulated through the food chain, when one organism eats another. Any remaining energy in dead organisms is consumed by decomposers.
Can energy be recycled?
As noted above, energy cannot be recycled, and is not recycled in an ecosystem. Instead, it flows in and out of the ecosystem. But matter does recycle in the biosphere, and this is where matter and energy move very differently.
How does solar energy affect the hydrosphere?
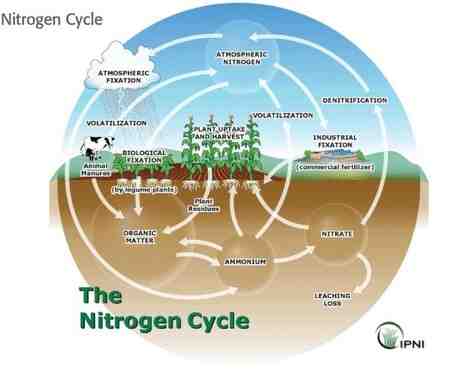
Driven by solar energy, surface water evaporates into the atmosphere, condenses, and falls back to the surface as precipitation, forming continents, creating rivers, and filling lakes. This process has eroded billions of tons of surface material from the continents into the oceans, forming major river deltas.
How does solar energy affect the biosphere? Most plants will not grow without energy from the sun. Solar arrays steal energy directly from the biosphere. Some of the incoming solar energy is reflected into space by the panels, some is converted into waste heat in the panels, and some is converted into electricity – most of it ends up as waste heat.
Does solar energy energize the hydrosphere?
Solar energy warms the hydrosphere. This is because the sun’s energy is absorbed by the water molecules in the hydrosphere causing it to vibrate…
Where does the energy that cycles water in the hydrosphere come from?
The sun is the main source of energy for phenomena on Earth’s surface, driving winds, ocean currents, and the water cycle.
How is solar energy connected to the water cycle or water pollution?
Solar energy heats surface water, causing evaporation; water vapor condenses into water droplets that form clouds, then falls back in the form of rain or snow; The falling water flows through rivers into the oceans for a repeating cycle.
What does solar energy have to do with the water cycle?
The water cycle is driven primarily by energy from the sun. This solar energy drives the cycle by evaporating water from oceans, lakes, rivers, and even land. Other water moves from plants to the atmosphere by the process of transpiration.
How does the hydrosphere interact with the sun?
When water is heated (eg by energy from the sun), it evaporates and forms water vapour. When the water vapor cools again, it condenses to form liquid water which eventually returns to the surface via precipitation e.g. rain or snow.
What does the hydrosphere interact with?
It is important to realize that the hydrosphere is not an isolated system, but rather interacts with other global systems, including the atmosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere. These interactions are sometimes known collectively as the water cycle.
How does the Sun interact with the biosphere?
The upper atmosphere protects biosphere organisms from the sun’s ultraviolet radiation. It also absorbs and radiates heat. This sphere is also where the weather occurs. Most Earth events involve interactions between multiple planes.
Is the hydrosphere affected by the Sun?
The sun is the main source of energy for phenomena on Earth’s surface, driving winds, ocean currents, and the water cycle. Energy from the Sun heats the Earth unevenly. As a result, convection currents develop in the atmosphere and the ocean.
How does solar energy affect the atmosphere?
The sun’s rays hit the earth most directly at and near the equator. The extra solar energy absorbed there heats the air, soil, and water. Heat from the soil and water is sent back into the air, heating it even more. Hot air rises.
Do solar panels damage the atmosphere?
Previous studies have shown that both solar arrays and wind farms have the potential to cause regional changes in temperature and precipitation by altering the amount of solar radiation absorbed by Earth or disrupting local airflow patterns.
How is most matter and energy cycled in the biosphere?
Food webs model how matter and energy are transferred among producers, consumers and decomposers when all three groups interact in an ecosystem. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration provide most of the energy for life processes.
How do energy and matter rotate through the sphere? Cycles of Matter on Earth Elements such as carbon interact chemically as they rotate through the globe. Like water, these elements cycle through Earth’s systems, ecosystems, and organisms. The sun and heat from within the Earth provide the energy that drives this cycle.
How does matter and energy flow in the biosphere?
Energy flows through all life on Earth. Plants use energy from the Sun to create organic matter. Plants are then eaten by primary consumers which are then eaten by secondary consumers, and so on. With each step, the energy originally emitted by the Sun was consumed, but that energy also dissipated with each step.
How does the flow of matter and energy happens in the biosphere?
Nutrients are taken up by plants through their roots. Nutrients are passed on to primary consumers when they eat plants. Nutrients pass to higher-level consumers when they eat lower-level consumers. When a living thing dies, the cycle repeats itself.
What is the flow of energy in the biosphere?
Energy Flow in the Biosphere The basic process of capturing solar energy and converting it into chemical energy available to all living organisms is photosynthesis. Through photosynthesis, plants convert inorganic inputs (carbon, water, nitrogen, phosphorus, etc.)
How is energy cycled in the biosphere?
Flow of Energy in the Biosphere Through photosynthesis, plants convert inorganic inputs (carbon, water, nitrogen, phosphorus, etc.) into the millions of different energy-rich organic materials that comprise all organisms.
What is cycled in the biosphere?
Life is built on the conversion of carbon dioxide into carbon-based organic compounds from living organisms. The carbon cycle illustrates the importance of carbon in the biosphere.
How does energy cycle in the environment?
The flow of energy occurs through food chains and food webs. During the process of energy flow in the ecosystem, plants as producers absorb sunlight with the help of chloroplasts and some are converted into chemical energy in the process of photosynthesis.
How does the biosphere get energy?
Energy from the Sun fuels life on Earth Sunlight enables plants, algae, and cyanobacteria to use photosynthesis to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds such as carbohydrates. This process is a fundamental source of organic matter in the biosphere.
How are matter and energy cycled in an ecosystem?
Dead producers and consumers and their waste products provide material and energy for decomposers. Decomposers convert matter back into inorganic forms that can be recycled in the ecosystem. So, the energy that enters the ecosystem as sunlight eventually flows out of the ecosystem in the form of heat.
How is matter cycled in an ecosystem?
Matter cycles between air and soil and between plants, animals, and microbes as these organisms live and die. Organisms obtain gases, and water, from the environment, and release waste material (gas, liquid, or solid) back into the environment.
How is matter and energy cycled?
What is the source of energy in ecosystem?
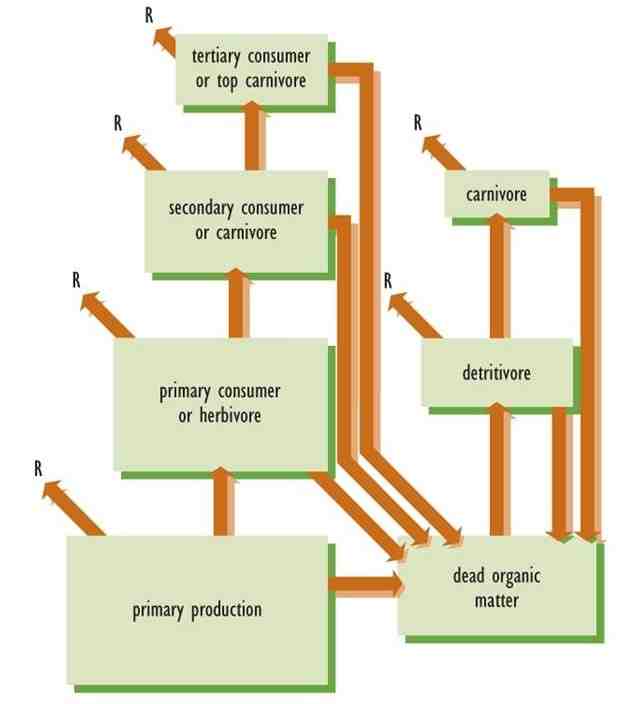
The main source of energy for almost every ecosystem on Earth is the sun.
Which of the following is the main source of energy for living things? 3.1 The sun is the main source of energy for organisms and the ecosystems of which they are a part. Producers such as plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use energy from sunlight to make organic matter from carbon dioxide and water. This establishes the beginning of the flow of energy through almost all food webs.
Which macromolecule is the main source of energy in cells?
Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital source of energy for cells, provide structural support for many organisms, and can be found on the surface of cells as receptors or for cell recognition.
Which macromolecule is made up of chains of monosaccharides?
Long chains of monosaccharides linked by covalent bonds are known as polysaccharides (poly- = “many”). The chains can be branched or unbranched, and may contain different types of monosaccharides. Polysaccharides may be very large molecules.
What are the 4 macromolecules?
11.1 Introduction: The Four Major Macromolecules These are carbohydrates, lipids (or fats), proteins, and nucleic acids. All major classes of macromolecules are similar, in that they are large polymers assembled from small repeating monomeric subunits.
Are monosaccharides considered macromolecules?
Carbohydrates are essential macromolecules classified into three subtypes: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.