An electrode coating just one molecule thick can significantly enhance the performance of an organic photovoltaic cell, KAUST researchers have found. The coating outperforms the leading material currently used for this task and may pave the way for improvements in other devices that rely on organic molecules, such as light-emitting diodes and photodetectors.
Unlike the most common photovoltaic cells that use crystalline silicon to harvest light, organic photovoltaic cells (OPVs) rely on a light-absorbing layer of carbon-based molecules. Although OPVs cannot yet rival the performance of silicon cells, they could be easier and cheaper to manufacture at a very large scale using printing techniques.
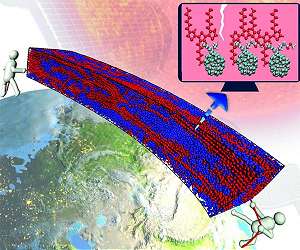
When light enters a photovoltaic cell, its energy frees a negative electron and leaves behind a positive gap, known as a hole. Different materials then gather the electrons and holes and guide them to different electrodes to generate an electrical current. In OPVs, a material called PEDOT:PSS is widely used to ease the transfer of generated holes into an electrode; however, PEDOT:PSS is expensive, acidic and can degrade the cell’s performance over time.
The KAUST team has now developed a better alternative to PEDOT:PSS. They use a much thinner coating of a hole-transporting molecule called Br-2PACz, which binds to an indium tin oxide (ITO) electrode to form a single-molecule layer. The organic cell using Br-2PACz achieved a power conversion efficiency of 18.4 percent, whereas an equivalent cell using PEDOT:PSS reached only 17.5 percent.
“We were very surprised indeed by the performance enhancement,” says Yuanbao Lin, Ph.D. student and member of the team. “We believe Br-2PACz has the potential to replace PEDOT:PSS due to its low cost and high performance.”
Br-2PACz increased the cell’s efficiency in several ways. Compared with its rival, it caused less electrical resistance, improved hole transport and allowed more light to shine through to the absorbing layer. Br-2PACz also improved the structure of the light-absorbing layer itself, an effect that may be related to the coating process.
The coating could even improve the recyclability of the solar cell. The researchers found that the ITO electrode could be removed from the cell, stripped of its coating and then reused as if it was new.
In contrast, PEDOT:PSS roughens the surface of the ITO so that it performs poorly if reused in another cell. “We anticipate this will have a dramatic impact on both the economics of OPVs and the environment,” says Thomas Anthopoulos, who led the research.
Related Links
King Abdullah University Of Science and Technology (KAUST)
All About Solar Energy at SolarDaily.com
|
We need your help. The SpaceDaily news network continues to grow but revenues have never been harder to maintain. With the rise of Ad Blockers, and Facebook – our traditional revenue sources via quality network advertising continues to decline. And unlike so many other news sites, we don’t have a paywall – with those annoying usernames and passwords. Our news coverage takes time and effort to publish 365 days a year. If you find our news sites informative and useful then please consider becoming a regular supporter or for now make a one off contribution. |
||
|
SpaceDaily Contributor $5 Billed Once credit card or paypal |
SpaceDaily Monthly Supporter $5 Billed Monthly paypal only |
|
![]()
Engineers apply physics-informed machine learning to solar cell production
Austin TX (SPX) Jun 10, 2021
Today, solar energy provides 2% of U.S. power. However, by 2050, renewables are predicted to be the most used energy source (surpassing petroleum and other liquids, natural gas, and coal) and solar will overtake wind as the leading source of renewable power. To reach that point, and to make solar power more affordable, solar technologies still require a number of breakthroughs. One is the ability to more efficiently transform photons of light from the Sun into useable energy.
Organic photovoltaics … read more
