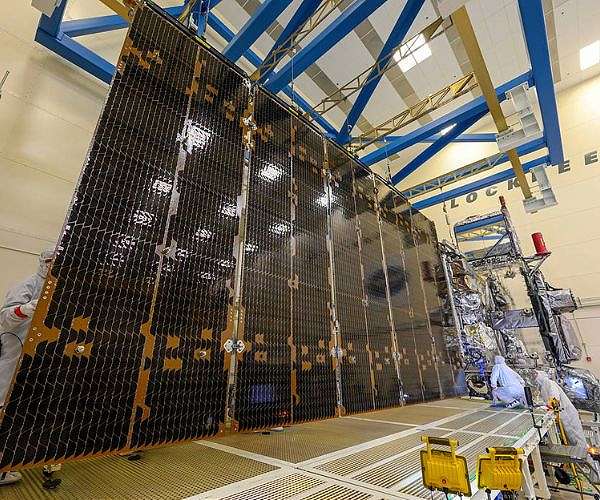
WASHINGTON – NASA is launching a study to re-examine the viability of space-based solar energy, a long-awaited solution to deliver power from space that could gain new interest through technological advances and push for clean energy.
In a presentation at the National Space Society’s International Space Development Conference May 27, Nikolai Joseph of the NASA Office of Technology, Policy and Strategy said that the agency is launching a short-term study evaluating the perspectives of space-based solar energy, or SBSP, the first by the agency in about two decades.
“As technology has evolved, the feasibility of the system has changed over time,” he said. “This study will assess the degree to which NASA should support space-based solar energy.”
The study will not try to come up with a new architecture for SBSP, but instead put forward concepts for collecting solar energy in space and transmitting it to the ground to convert electricity. These updated systems are compared to terrestrial power systems and assess the policies and implementation challenges they face.
It will also look at the cost of such systems, which have traditionally been a major stumbling block in previous studies from the 1970s. “There will be a lot of money, but money is not the only driver here,” he said. “If the number is huge and surprising, that may be OK.”
Advances in various technical areas, Joseph said, give the agency reason to at least re-examine the feasibility of the SBSP. “The elephant in the room is start-up costs, and the start-up has become significantly more accessible. That completely changes the way we look at it,” he said. Other areas that have seen progress include thermal systems, electronics, materials and solar panels.
NASA has had discussions with the U.S. Space Force and other “technical agencies” about the study, he said. There are no plans at present to seek public input through a formal request for information or any other process, but he did not rule out doing so later. The aim is to complete the study and present it at the International Astronautical Congress in Paris in September.
There has been a resurgence of interest in the SBSP in recent years, including a workshop last December by the European Space Agency, which Joseph said NASA participated in and which led the agency to consider its own study. The British government included SBSP as a technology that it explored in addition to nuclear, wind and other energy systems last year.
Much of that interest is driven by the desire for energy sources that can achieve “zero-zero” carbon emissions targets to reduce climate change. “I think it’s one of the most promising things we can do from a space perspective to save the planet. We need to get to zero by 2050,” said Karen Jones of The Aerospace Corporation’s Center for Space Policy and Strategy. a later panel on SBSP at the conference.
“It just makes no sense for the U.S. not to look at this,” said Peter Garretson, a former U.S. Air Force officer who led a 2007 SBSP study of the now-closed National Security Space Office. cites both climate change and international competition, including reported Chinese interest in SBSP.
“Even if you assume that solar energy in space is not economical, the fact that we’re losing history by not trying something on a global agenda just makes us look stupid,” he argued.
John Mankins, a longtime lawyer for SBSP, who conducted previous NASA studies on the subject, said “super-cheap” space access promised by vehicles like SpaceX’s Starship changed the economy of such a system. “Transportation is no longer part of the cost equation,” he said. “That makes space solar energy potentially affordable, depending on how you do it.”
In his speech, Joseph said that the study, in addition to looking at costs and political issues, also examines the public perception of space-based solar energy. “Public perception is something we don’t talk about much,” he said, noting that when he explains how such systems radiate power back to Earth, people ask what that means for birds flying through these carriers. “I do not think it will be a problem, but I do not know it completely and I have to understand it.”
He said the study offers benefits even if it concludes that SBSP is not feasible. “It’s a wonderful straw man to understand how we tackle big problems like that,” he said. “It’s also a great way to look at how you build policies around big projects.”
“I think there is something of an obligation within NASA to look into this,” he added, “because it has been around for so long and this idea has not yet been destroyed. It is permanent.”
Quelle est la taille de la sonde Parker ?

The probe, the size of a small car and endowed with four instruments, collects data on the thermal mechanism that drives the Sun’s crown and accelerates the solar wind, a constant flux of ionized particles up to 500 km / s . On the same subject : Namibia comes to Europe to sell its sunshine.
Where’s the Parker probe? The Parker probe enters the atmosphere of the Sun. And the exploit is size, even if it is the layer that is the most external of the atmosphere, the solar crown.
Quelle est la température à la surface de Vénus ?
Due to this proximity, Venus receives about 2 times more energy from the Sun than the Earth. This may interest you : Why solar energy is bad ?. However, it is not for this reason that its surface appears to have an average temperature of 462 ° C, even more so than 400 ° C are considered required for an ideal pizza oven (traditional Neapolitan recipe).
Quelle est la température à la surface de Vénus le jour et la nuit ?
The temperature at the surface of Venus is very elevated (737 K = 474 ° C) and does not present almost any diurnal variation. The temperature of the sun is near 460 ° C. The temperature profile between 0 and 100 kilometers differs notably from the terrestrial profile.
Quelle est la température de Vénus la nuit ?
However, it is not even at altitude, where the atmosphere is much lighter: at 100 km, the temperature varies even from 29 ° C during the day to 143 ° C at night.
Quelle est la température la plus froide de Vénus ?
| Orbital characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Equilibrium temperature of the black body | 226.6 K (46.4 ° C) |
| Temperature of the surface | |
| â € ¢ Maximum | 763 C (490 ° C) |
| â € ¢ Average | 737 K (464 ° C) |
Quelle est la couleur de la planète Vénus ?
Venus presents an internal structure similar to that of the Land: Croûte, Manteau and Noyau. Aged 4,503 billion years ago, it can be reconciled with its spacious atmosphere that hides all its surface, and its characteristic colors that turn yellow to orange.
Quel est la couleur de la planète Saturne ?
This planet has an unparalleled car appearance it has orange and maroon bands with other white bands.
Est-ce que Vénus est l’étoile polaire ?
The Polar star and the Berger star are two distinct stars. The Polar star is indeed a star while the Berger star is a planet, Venus.
Pourquoi Vénus est appelée Létoile du berger ?
In popular culture, the planet Venus is known as the “star of Berger” because it can be easily seen in the sky of the morning (east), before the aurora, or in the sky of the evening (in the evening) ) west), after the crepuscule.
Pourquoi la température de surface de Vénus est si élevée ?

However, the presence of greenhouse gas effects such as SO2, water particles, sulfuric acid as well as carbon dioxide provoke an important greenhouse effect. That’s the reason for it, it’s hot on the surface of Venus. This heater also explains the absence of water on the surface.
Why the temperature of Venus? The surface density is 65 kg / m3, which represents 50 times the density of the terrestrial atmosphere at 293 K (20 ° C) at sea level. This Atmosphere, rich in carbon dioxide, is the origin of the most powerful effect of conservatory of the Solar System, creating surface temperatures of around 735 K (462 ° C).
Quelle est la force gravitationnelle de Vénus ?
Quelle est la particularité de Vénus ?
It takes the Sun’s turn in a little less than 225 terrestrial days. This planet is marked by two important details: “it is the only one that rotates in the sense of the eyes of a display case”, but also to take “more time to make a rotation on its axis than to turn around the Sun” .
Quelle est la forme de Vénus ?
Venus possesses the most circular orbit of the planets of the Solar System with an orbital eccentricity near zero and, as a result of its slow rotation, is almost spherical (aplatement considered as zero).
Quelle est la pression de Vénus ?
At sunset the atmospheric pressure is 95 bars and the temperature up to 470 ° C.
Pourquoi la température de Vénus est plus élevée que celle de Mercure ?
Mercury has no more atmosphere, unlike Venus which is endowed with an atmosphere rich in carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid nuances. This atmosphere preserves the heat, thanks to a phenomenon that is well known on Earth: the effect of conservancy.
Quelle est la planète la plus chaude de l’univers ?
Venus, the star of Berger Prussia is also as large as our planet, it is known as the twilight of the Earth. But Venus is the planet where it is the hottest, at 462 ° C.
Quelle est la particularité de la planète Vénus ?
It takes the Sun’s turn in a little less than 225 terrestrial days. This planet is marked by two important details: “it is the only one that rotates in the sense of the eyes of a display case”, but also to take “more time to make a rotation on its axis than to turn around the Sun” .
Quelle est la planète la plus proche du Soleil Vénus ou Mercure ?
The telluric planets, on solid surfaces, near the Sun are, by distance order to our star, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. The more elusive and galactic planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are.
Pourquoi la température moyenne de Vénus est très supérieure à la température de la terre ?
As an information source, the terrestrial atmosphere contains 77% Azote and 22% Oxygen. The elevated density of the atmosphere is partly responsible for the climatic conditions on Venus.
Pourquoi la température moyenne de la Terre augmente ?
Today, temperatures are maintained at their elevated level essentially due to the accretion of gas conferences having an effect on the atmosphere, in particular carbon dioxide (CO2), according to Nasa.
Pourquoi la température réelle sur Terre Est-elle supérieure à sa température théorique ?
The difference between the theoretical temperature and the actual temperature depends on the thickness of the atmosphere, its density (atmospheric pressure) and its composite in gas to the effect of conservatory.
Pourquoi Vénus à une température plus élevée que la Terre ?
The secret of the Venetian furnace resides in the atmospheric space of this planet composed of 96.5% of CO2 where the effect of conservatory associated with this gas is packaged.
How does the Parker Solar Probe not melt?
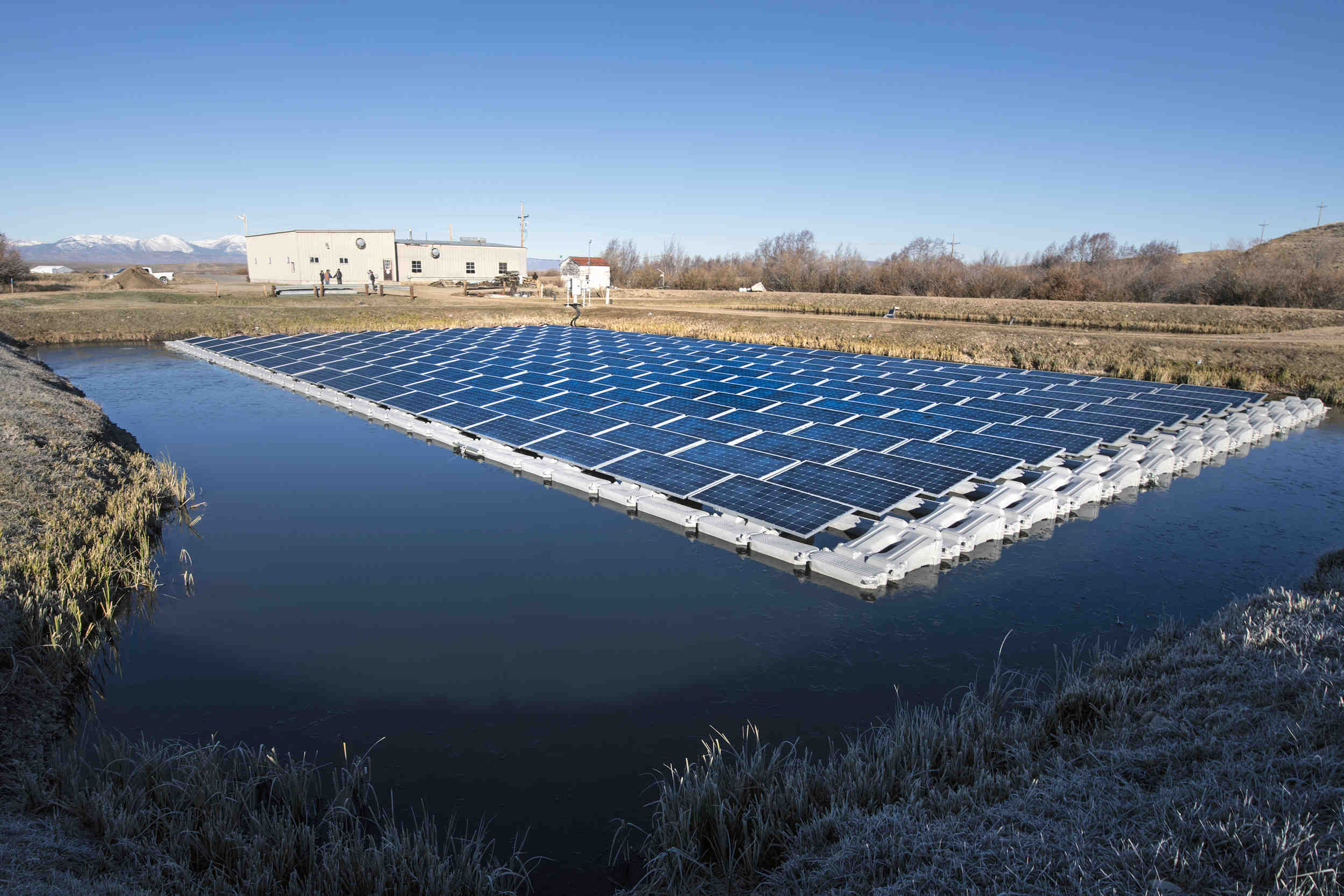

The Parker Solar Probe is the closest spacecraft to the Sun, and it is able to survive extreme temperatures due to a thermal shield made of carbon composite material, withstanding up to 2,500 degrees Fahrenheit or 1,377 degrees Celsius.
Où se trouve la sonde Parker ?
Mission of 7 years The Parker solar probe left the Earth in the month of August 2018. Its primary mission will last for seven years, with an end awaiting in 2025. But its operational career could be extended.
What is the speed of the Parker probe?
Où est Parker Solar Probe ?
After two other surviving Venus, in 2023 and 2024, the Parker spacecraft will have a distance of only 6.2 million kilometers from the Sun, at a speed close to 700,000 km / h.