A Massachusetts renewable energy company hopes to help low-income consumers access the financial benefits of clean energy nationwide with a new platform that allows homeowners to share excess solar credits.
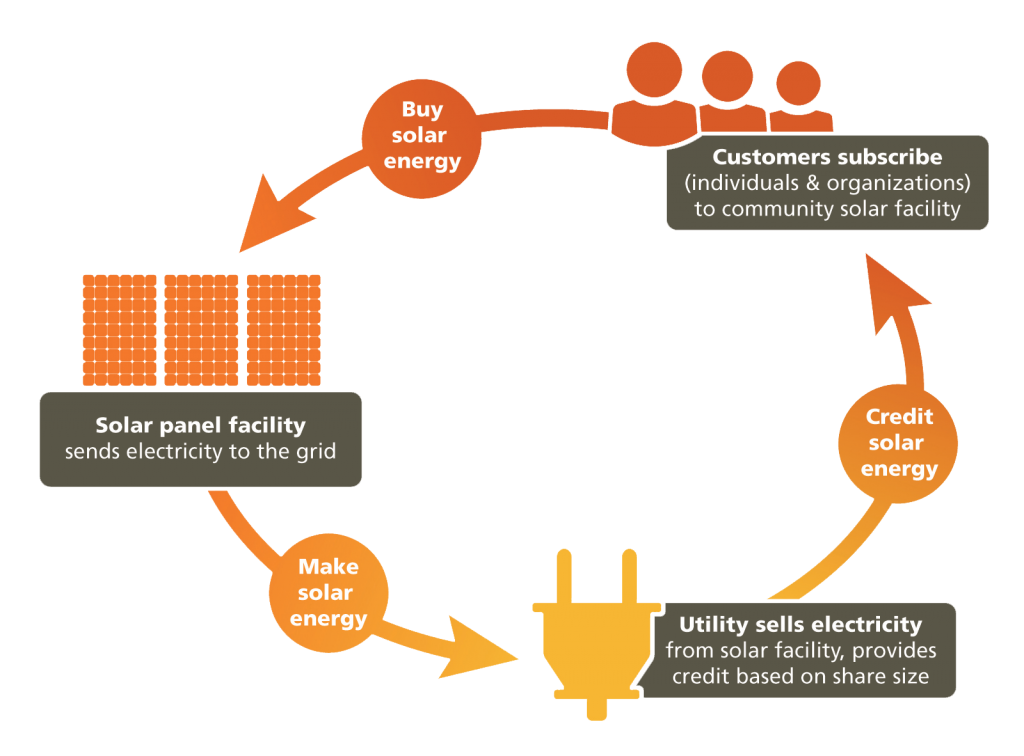
The Solar Equity Platform, created by Boston-based Resonant Energy, encourages homeowners with enough space to install systems that outsize their homes. Homeowners will receive state incentives for the power generated, while credits generated from additional energy production are passed on at no cost to low-income residents, who can use them to offset their electricity bills.
“We take people who have the structural advantage of having large homes and leverage that asset,” said Ben Underwood, co-founder and co-CEO of Resonant Energy. “It’s taking some of that value and sending it to people in low-income neighborhoods.”
Currently, the platform is only operating in Massachusetts. However, Resonant hopes to expand the concept to other states as well. And it’s not just its creators who see the promise of the idea: the platform made it to the final round of the US Department of Energy’s American Made Solar competition.
While solar power is on the rise across the country — solar installations accounted for half of the new electric generation capacity added nationwide in 2021, according to the Solar Energy Industries Association — low-income households are often left out of that progress. The initial costs of installing a system are often too high for a family struggling to pay the bills. Low-income consumers are also more likely to live in rental units or in homes with older roofs or outdated electrical systems that don’t support solar panels.
In an effort to close that gap, Massachusetts’ solar incentive plan, the Solar Massachusetts Renewable Target program (SMART), provides additional money for home systems for low-income families, as well as those that allocate some or all of their clean energy. produced to low-income households, allowing these residents to benefit from stable and lower electricity prices.
So far, however, this incentive has had a limited impact: only 10% of the capacity for which the program has received requests have applied for some form of these incentives.
The Solar Equity Platform is designed to increase these numbers by simplifying the process of building and sharing excess capacity.
“Energy production is such a big part of the economy that as we move to a more distributed system it would be a real loss not to capture some of that for people who haven’t benefited from energy production before,” Underwood said.
Spark of an idea

The idea for the platform first came to Underwood almost two years ago, when he was thinking about buying a house. As she thought about the disparities in access to housing, she wondered why there wasn’t a system in place to pay off her extra mortgage and use that money to pay off the mortgages of people who need it. To see also : Astronauts install new rollout solar panels on International Space Station. He quickly realized that he could apply this idea to his solar energy business in a very real way.
Founded in 2016, Resonant is a solar developer focused on building systems to benefit disadvantaged communities. To date, the company, a registered B Corporation, has completed more than 160 projects, most of which serve low-income households, churches and non-profit organizations. The idea of finding ways to share solar energy was a natural fit for the company’s mission.
When a home with a solar array generates more power than it consumes, the homeowner receives a credit on the bill for the additional power shared with the grid. Often, however, homeowners accumulate these credits and don’t need to use them because their solar systems provide enough power that they rarely need to go off the grid.
Underwood envisioned a platform that would allow those solar credits that would otherwise go unused to be shared without having to work through a jumble of paperwork and regulations. Resonant worked with Boston-based software developer MySunBuddy to make this vision a reality.
Solar installers will recruit homeowners into the program when they find new customers who have enough roof space for a system that’s too large or whose existing solar-powered homes regularly generate more energy than they need.
“The idea would be to empower supply installers to bring their customers onto the platform without our direct involvement,” Underwood said.
Ideally, the system will provide financial benefits to all participants. Resonant will take a small fee each time an installer signs up a new system for the program, generating low-effort income. Installers will earn more by installing larger systems. System owners will receive enough money from state incentives to make a return on their investment in a larger system.
Participating low-income households will also see significantly lower electricity bills, Resonant estimates. The idea is to match a contributing household with a receiving household. Depending on the size of the typical residential facility, low-income recipients will see savings of $300 to $500 per year.
To distribute the donated credits, Resonant seeks to work with grassroots community groups that can use the availability of clean energy credits to sweeten and strengthen other energy-saving offerings. For example, homeowners interested in weatherization can be given credits, often provided at no cost by state efficiency programs.
“People are taking significant action through the weather,” Underwood said. “That might make it more worth doing.”
Resonant is talking to area nonprofits about getting involved, but clean energy nonprofit Green Energy Consumers Alliance is already on board. The organization has a fund to help low-income families pay their heating bills in the winter; Executive Director Larry Chretien expects the Solar Equity Platform to serve as a clean energy complement to the existing program.
“Our organization believes it is important to bring the benefits of clean energy to everyone,” said Chretien. “And we want to explore different ways to do that.”
Scale of impact

While the Solar Equity Platform doesn’t change some of the underlying structural challenges that make solar power less accessible to low-income households, it does try to get the most benefit and equity out of the current system, supporters said. On the same subject : Flex solar san diego.
“We’re trying to take advantage of the fact that there are people with additional solar capacity,” Chretien said. “A good roof is a terrible thing to waste.”
For Homeowners Rehab Inc., a nonprofit affordable housing developer based in Cambridge, participating in the Solar Equity Platform will help advance its commitment to solarize as many of its 70 properties as possible, said Will Monson, CEO of the project.
“As the Solar Equity Platform increases yield, it allows us to deploy the limited amount of funds we have available to more projects,” said Monson.
The availability of the platform can also help solar installers by giving homeowners an extra moral and financial motivation to commit to a larger system, said Casey Bolduc, director of marketing and technology for ACE Solar.
“Being able to offer that to our clients as an additional financial angle and the feeling of contributing to the greater good – I see that as a potential benefit that will help someone who’s interested get over the hump,” Bolduc said. .
The platform has been running in Massachusetts for about two months. A customer has signed in to share their credits and others are ready.
In Massachusetts alone, if just 10 percent of new solar installations went on the platform, about 1,100 low-income households would save about $500,000 a year, he estimated.
And Underwood is already exploring options for expanding the model to other states, where solar incentives and net metering would make the economy work. Resonant has begun researching community groups and other potential partners in the New England states in preparation for this planned expansion.
In the meantime, they will work to expand and strengthen participation in Massachusetts so that potential participants in other states can clearly see the benefits of the platform.
“We hope to explain why it’s good for other states, why it makes economic sense,” Underwood said.
How long do solar panels last?

Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic or photovoltaic panels, are made to last for more than 25 years. In fact, many solar panels installed in the 1980s are still operating at their expected capacity. Not only are solar panels very reliable, but the lifespan of solar panels has increased dramatically over the past 20 years.
What are the 2 main disadvantages of solar energy? Disadvantages of Solar Energy
- the cost The initial cost of purchasing a solar system is quite high. …
- Depends on the weather. Although solar energy can still be collected on cloudy and rainy days, the efficiency of the solar system decreases. …
- Solar energy storage is expensive. …
- Uses a lot of space. …
- Related to pollution.
How long do solar panels take to pay for themselves?
The most common estimate for the average payback period for solar panels is six to ten years. This is quite a wide range as there are many factors that will affect the number of years it takes to pay off your panels and the monthly savings you can expect.
Will a solar system pay for itself?
Will solar panels ever pay for themselves? On average, it takes between nine and 12 years for solar panels to pay for themselves. Over the years, you can recoup the initial costs of your investment, and then continue to save on your energy bill.
How long does it take to break even on solar panels?
For most U.S. homeowners, it takes approximately eight years to recoup their solar panel investment. For example, if the cost of your solar installation is $16,000 and the system saves you $2,000 annually on your energy bill, then the payback period will be eight years (16,000/2,000 = 8).
How long does a solar system take to pay for itself?
Solar panels pay for themselves over time by saving you money on your electricity bill and, in some cases, making you money through ongoing incentive payments. The average payback time for solar panels in the United States ranges from 5 to 15 years, depending on where you live.
How often do you replace solar panels?
The industry lifespan is about 25 to 30 years, which means that some panels installed at the beginning of the current boom have not been retired for a long time.
How often should I replace solar panels?
Solar panels can operate for 20 to 30 years. Beyond that, they begin to degrade, and their output will be significantly reduced because the silicon photovoltaic material of the panel will effectively convert light into electricity.
Do solar panels require a lot of maintenance?
Solar panel systems are very durable and require little maintenance during their productive life, which can last 25 years or more. If something goes wrong, the components of your solar PV system have very long warranties that would cover replacement and repair costs.
Do solar panels still work after 25 years?
The industry standard for the productive life of a solar panel is 25-30 years. However, a solar panel will not die after 25-30 years, on the contrary, their production will be significantly reduced below what the manufacturer planned.
Do solar panels lose efficiency over time?
The efficiency of solar panels is higher than ever, but the amount of electricity the panels can generate still decreases gradually over time. High-quality solar panels degrade at a rate of about 0.5% each year, producing about 12-15% less power at the end of their 25-30 lifetime.
How efficient are solar panels after 20 years?
For a while, the general rule was that panel production degraded at a rate of about 1% per year, compounded. This meant that a panel could be expected to operate at 82% efficiency after 20 years, 74% after 30 years and 66% after 40 years.
How efficient are 10 year old solar panels?
According to a 2012 study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory [PDF], the average rate of panel degradation is between 0.5% and 0.8% per year. Degradation rate is the rate at which solar panels lose efficiency over time. A panel with a degradation rate of 1% per year will be 10% less efficient after 10 years.
Why do solar panels lose efficiency over time?
Over time, solar panels lose their ability to absorb sunlight and convert it into solar energy due to warmer weather and the natural reduction of chemical power inside the panel. This is the so-called âdegradation rateâ. The lower the degradation rate, the better the panel.
Do solar panels work in New England?
As you probably know, New England has a wide range of weather, from sunny weather to rain, snow, and hail. Solar panels are built to withstand all of these conditions, but of course they will draw more energy on brighter, brighter days.
How long do solar panels last in New England? In general, solar panels are very durable and with no moving parts, they will generally require little or no maintenance. So far, the average lifespan of residential solar panels is around 25-30 years. However, some systems can last 50!
Do solar panels make sense in Massachusetts?
Solar panels not only make sense in Massachusetts, but the state also offers incentives for homeowners who use this renewable resource. The Massachusetts Clean Energy Center highlighted eight incentives and programs for residents to take advantage of.
Do solar panels increase home value in Massachusetts?
In Massachusetts, you can expect solar panels to increase your home value by up to 2-3%, depending on how much your home is worth, the size of your solar system, and the exact location in Massachusetts where you live.
Does solar make sense in New England?
While the grass is always greener on the other side, and the sun always shines brighter in the retirement states, New Englanders have no problem maintaining healthy gardens and pastures, and we can easily get the sun to be reasonable (and less expensive than yours). local availability) possibility of energy production.
Is Massachusetts a good state for solar?
Many people believe that solar systems do not work in Massachusetts because of the varied weather conditions in New England. However, experts agree that Massachusetts is an excellent location for solar systems.
Does solar work in Massachusetts?
Many people believe that solar systems do not work in Massachusetts because of the varied weather conditions in New England. However, experts agree that Massachusetts is an excellent location for solar systems.
Will Massachusetts pay for solar panels?
Incentive Programs, Tax Credits and Solar Rebates in Massachusetts* A 26% federal solar tax credit is available for home solar systems purchased through December 31, 2022. A 15% state solar tax credit is available for home solar systems purchased.
Are solar panels really free in Massachusetts?
But unfortunately, there are no free solar panel installations in Massachusetts, despite what you may have seen online.
How much does it cost to put solar panels on your house in Massachusetts?
According to Save On Energy, a solar panel system in Massachusetts costs between $3 and $5 per watt. The average solar system size for home use is five kilowatts, and the average solar system cost is between $15,000 and $25,000.
Is solar worth it in the Northeast?
Solar power is most efficient in areas with consistent and reliable sunlight. However, a recent study of homeowners’ savings with solar energy found that the systems were very effective even in the Northeast.
Are solar panels worth it in New York State?
Solar panels provide greater value where energy consumption or energy rates are high. New Yorkers use less electricity than most US residents, but pay significantly higher prices for the electricity they use. Thus, solar is very valuable in New York and is considered a great investment.
How effective are solar panels facing east?
Assuming a standard square foot roof, east and west facing panels produce 15% less electricity, and north facing solar panels produce 30% less energy.
Is solar for your home really worth it?
Recently, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) found that for a home with a solar energy system, every dollar saved in energy increases a home’s value by $20. The return on investment (ROI) is 20 to 1. Here are some factors to help maximize the value of your solar investment.
What are the solar incentives in Massachusetts?
A 26% federal solar tax credit is available for home solar systems purchased installed by December 31, 2022. A 15% state solar tax credit is available for home solar systems purchased in Massachusetts. (Up to a $1,000 state tax deduction).
How do I apply for the Massachusetts solar tax credit? To get started, you’ll need to fill out IRS Form 5695, Home Energy Credits. Form 5695 is used to calculate tax credits for home energy improvements, including solar panels, geothermal heat pumps, wind power, and more.
Can you get free solar in Massachusetts?
We’d love to live in a world where free solar power for your home is a reality. When you own your own solar panels, you can generate free renewable energy to power your home. But unfortunately, there are no free solar panel installations in Massachusetts, despite what you may have seen online.
How much does it cost to get solar panels in Massachusetts?
According to Save On Energy, a solar panel system in Massachusetts costs between $3 and $5 per watt. The average solar system size for home use is five kilowatts, and the average solar system cost is between $15,000 and $25,000.
Can you get solar panels fitted for free?
Can I still get free solar panels in 2022? The short answer is no, unfortunately. It’s hard to believe that when the Feed-in Tariff started in 2010, companies would literally buy your solar panels from you.
Is solar tax exempt in Massachusetts?
Summary Massachusetts law provides that solar energy systems and wind energy systems used as energy systems to heat or otherwise supply the energy needs of taxable property are exempt from local property taxes for a period of 20 years.
Does Massachusetts pay for solar panels?
Under the program, the State of Massachusetts pays Eversource, National Grid or Until customers a fixed rate for each kilowatt-hour of electricity produced by the solar panel system. This rate ranges from $0.19 to $0.31 per kilowatt hour, depending on your location and electric utility provider.
How much does it cost to put solar panels on your house in Massachusetts?
According to Save On Energy, a solar panel system in Massachusetts costs between $3 and $5 per watt. The average solar system size for home use is five kilowatts, and the average solar system cost is between $15,000 and $25,000.
Does Ma have a solar credit?
Massachusetts has a solar tax credit called the Renewable Energy Income Tax Credit. Homeowners can claim this credit in their state tax credit, which is worth 15% of the cost of the solar system (up to a $1,000 tax credit).
Does solar make sense in Massachusetts?
Massachusetts is among the most solar-friendly states in the US. According to data from the Environment Massachusetts Research and Policy Center, Massachusetts has the sixth largest solar capacity in the nation. As of July 2021, the average solar panel in Massachusetts will cost you $3.10 per watt.
Will there be solar incentives in 2022?
Solar photovoltaic systems installed in 2020 and 2021 are entitled to a 26% tax credit. In August 2022, Congress approved an extension of the ITC, increasing it to 30% for installation from 2022-2032.
Is there an energy tax credit for 2022?
Tax credits for residential energy efficiency and energy efficient home builders were retroactively extended until December 31, 2022.
Will solar panels be cheaper next year?
Solar costs rose in 2021 in part due to supply chain constraints, according to a report released Thursday by the Solar Energy Industries Association and Wood Mackenzie. The price increase is the first since Wood Mackenzie began tracking the data in 2014.
How does the solar 26% tax credit work?
What is the Solar Tax Credit? If you install solar energy equipment on your home by the end of 2032, you are eligible for a refundable income tax credit of 30 percent of eligible expenses.
Do solar panels work on cloudy days?
Photovoltaic panels can use direct or indirect sunlight to generate energy, although direct sunlight is the most efficient. Solar panels will work even when clouds reflect or partially block the light. Rain helps your panels work efficiently by washing away any dust or dirt.
How effective are solar panels on a cloudy day? It is estimated that most solar panels operate at 50% of their normal efficiency in foggy conditions…very dense cloud cover or overcast conditions.
Do solar panels charge on rainy days?
Solar PV System Efficiency and Rain The good news is that your solar PV system will continue to produce energy even when it’s raining and cloudy. Solar panels installed on your roof can use direct or indirect sunlight, but they are most effective when they receive direct sunlight.
Do solar panels produce electricity on cloudy days?
Does a cloudy day affect the generation of solar energy? Anyone who has been sunburned on a cloudy day knows that solar radiation penetrates the clouds. For the same reason, solar panels can still produce electricity on cloudy days.
What happens to solar panels when it rains?
The rain itself will not affect your solar power system. Solar panels are waterproof, so moisture will not damage them. And indeed, the rain is helpful, as it will wash away some of the dirt and debris that accumulates on the panels over time.
Do solar panels work on stormy days?
Yes, solar panels can work on cloudy and rainy days, but not always at their peak performance. Their effectiveness depends on the level of cloud coverage. Anything that blocks sunlight from solar panels can reduce energy production, including clouds, fog, and tree shade.
Which solar panels work best on cloudy days?
Monocrystalline solar panels are the best solar panel technology for cloudy days. These solar panels are more efficient and perform better than other technologies in low-light conditions, such as cloudy days. Monocrystalline is also the most expensive type of panel.
Which solar panel is best in low light conditions?
Monocrystalline Panels Among the three basic types of solar panels – monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and amorphous – monocrystalline is the most efficient at collecting solar energy, and therefore somewhat more efficient in regions with sunlight.
How much solar power does a cloudy day need?
Do solar panels work on cloudy days? The simple answer is that solar panels work on cloudy days – they just don’t work as well on a sunny day. Although estimates range, solar panels will produce about 10–25% of normal power on a cloudy day.
How do solar panels work if there is no sun?
Cold and hot temperatures Solar panels absorb sunlight – the sun’s heat – and convert it into usable electricity. PV Semiconductors offer greater resistance in extreme heat, making the modules less efficient when they should be most efficient.
Do solar panels still work at night?
Solar panels work hard all day to generate electricity from the sun. They also support sustainable solar energy solutions at night. After sunset you can continue to benefit from their energy production through net metering and solar battery storage.
Can solar panels work without sunlight?
Solar panels work in direct sunlight, but they can also work without it. Solar panels produce electricity from a combination of direct and indirect sunlight as input. Both forms of sunlight carry photons, which are converted into electrical current by solar panels.



