AUSTIN — One of the recommendations that a little-known group of fossil fuel and electricity industry insiders has for Texas lawmakers would likely increase the cost of generating wind and solar power in the state.
Under Senate Bill #3 last year, the Legislature called for a new State Energy Plan Advisory Committee to make recommendations for the future of Texas’ power grid.
The members, led by Governor Greg Abbott, Lt. Gov Dan Patrick and House Speaker Dade Phelan met just twice at the Lower Colorado River Authority headquarters in Austin to produce a 100-page report, which narrowly passed. 7-5, with little thought.
Lawmakers could rely on the report during next year’s legislature, when lawmakers are expected to consider additional grid legislation to fix outages that caused power outages and killed more than 200 people in February 2021.
The report concludes that the Texas power grid has become more vulnerable due to the increasing importance of wind and solar power, also known as intermittent power, in Texas with its more than 1,000 power generation plants. Over the past decade, wind has grown to become the second most important source of energy in Texas, behind natural gas, which continues to power about half of the power grid.
Solar is also on the rise in Texas and could explode as an energy source due to new subsidies in the Inflation Reduction Act passed by Congress last month. A recent report by the Electric Reliability Council of Texas found that about half of new electric projects in Texas are solar, while only about 5% are natural gas.
However, the committee’s report warns that the grid is becoming overly dependent on intermittent power sources and batteries.
“The more power systems that rely on wind, solar and battery storage systems, the greater the risk that a major grid disruption will cause the grid to go into a blackout state,” the report said.
The conclusion contradicts studies by the University of Texas and the Federal Electric Regulatory Commission, which found that freezing power plants and natural gas wells and pipelines are the leading causes of power outages during the winter storm. A report commissioned by the natural gas industry disputes these findings.
The committee’s report recommends requiring wind and solar power to supplement their generation capacity by purchasing or generating “distributable” power to make up for lost production when the wind isn’t blowing or the sun isn’t shining. Deliverable energy generally refers to energy that can be activated at the flick of a switch, with natural gas being the most common source.
As part of the report, committee member Joel Mickey, an Austin-area energy consultant and former head of grid operations at ERCOT, wrote that the dispatchable requirement was “discriminatory” and “ignored ERCOT’s fundamental purpose.”
Mickey said if renewable energy producers were forced to buy large amounts of electricity from competitors, thousands of megawatts of existing renewable resources would be shut down and new producers would be discouraged from joining the ERCOT grid.
“Both outcomes will reduce ERCOT’s reliability and increase the likelihood of emergencies or rotating failures,” he wrote.
Retired Houston banker Mark Ammerman, one of Patrick’s committee appointments, also wrote dissentingly, saying the group’s work was incomplete and its effectiveness was doomed from the start.
“The [legislators’] report that is being presented, which sets out the work of this committee, is inadequate. There are several things that have not been studied but are evident to the members of the committee,” Ammerman wrote, noting, among other things, that the committee never heard testimony about battery storage at any of its meetings.
Many of the other recommendations in the report are similar to provisions in electricity grid legislation, which was passed in 2021 and is ongoing. Senate Bill 3 author Georgetown Republican Senator Charles Schwertner has described the State Energy Plan Advisory Committee as a back-up in case the Public Utility Commission fails to address grid outages.
The PUC has been fairly active, however, as commissioners plan major improvements to the Texas grid through a market transformation that prioritizes resilience versus cheap power that could drive up costs.
Philip Jankowski, Correspondent for the Austin Bureau. Philip Jankowski has been involved with Texas government, politics and criminal justice for 13 years. He previously worked for the Austin American-Statesman, the Killeen Daily Herald and the Taylor Press. Philip is a graduate of the University of Texas-Austin.
philip.jankowski@dallasnews.com PhilJankowski
The main reason oil production isn’t picking up is that US energy companies and Wall Street investors are unsure that prices will stay high long enough to turn a profit from drilling many new wells.
What is the total energy consumption in Texas?

Annual Energy Use Electricity: 365. On the same subject : On the way towards large-scale thermal storage systems.1 TWh (10% total in US) Coal: 98,300 MSTN (11% total in US) Natural gas: 3,377 Bcf (14% total in US) Motor gasoline: 303,100 Mbarrel (10% total in US US) Distillate Fuel: 164,500 Mbarrel (12% US total)
How many megawatts does Texas have? In 2019, Texas had a total summer capacity of 125,117 MW across all of its power plants and net generation of 483,201 GWh.
How much electricity does Texas use in a day?
At the same time, your power consumption increases. According to data from the US Energy Information Administration (EIA), the average Texan used 1,176 kWh per month in 2018. To see also : DoE grant will fund research into solar energy and power grids. This corresponds to about 39.2 kWh in a 24-hour period.
How many megawatts of electricity does Texas use?
| article | value | rank |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Power Source | natural gas | |
| Net summer output (megawatts) | 128,947 | 1 |
| power company | 27,948 | 3 |
| IPP & CHP | 100,999 | 1 |
How much electricity consume in a day?
This means that the average household electricity consumption in kWh per day is 28.9 kWh (867 kWh / 30 days).
How much electricity does a Texas home use?
The average Texas home uses 1,176 kWh per month, or 14,112 kWh per year, based on EIA data.
How many megawatts Does Texas consume?
Data shows that Texas consumes approximately 38,490,458 MWh of electricity.
How much power does Texas use daily?
At the same time, your power consumption increases. According to data from the US Energy Information Administration (EIA), the average Texan used 1,176 kWh per month in 2018. This corresponds to about 39.2 kWh in a 24-hour period. In the same year, the average price paid by customers was 11.2 cents per kWh.
How many megawatts of electricity does Texas use?
| article | value | rank |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Power Source | natural gas | |
| Net summer output (megawatts) | 128,947 | 1 |
| power company | 27,948 | 3 |
| IPP & CHP | 100,999 | 1 |
What is the largest source of energy consumption in Texas?
| fuel | GWh generated | proportion of total |
|---|---|---|
| natural gas | 181,770 | 47.4% |
| Money | 77,857 | 20.3% |
| wind | 76,708 | 20.0% |
| Nuclear | 41,314 | 10.8% |
How much of Texas power is nuclear?
Nuclear power accounts for less than 5% of Texas’ total electric capacity but produces nearly 10% of the state’s electricity, third behind natural gas and coal. The Lone Star State exports about 2% of the electricity it generates. There are two operating nuclear power plants in Texas.
What percentage of US energy comes from Texas?
Texas produces more electricity than any other state and generates almost twice as much as second-place Florida. In 2021, Texas accounted for about 12% of the nation’s total net electricity generation.
Which renewable energy resource is widely used in the state of Texas?
Texas is widely recognized as a leader in wind power – generating nearly 6 million megawatts of its total renewable energy from this source in November. That’s almost 27 percent of US wind power produced this month and 175 percent more than second-place Oklahoma.
Where does Texas rank renewable energy?

Texas: No. 1 in wind energy, generating nearly three times as much as the next state. And it is the fifth in solar power generation.
.
What percentage of renewable resources did Texas use for electricity in 2020?

The rise of renewable energy in Texas raises questions about the adequacy of power generation. Renewable electricity accounted for a quarter of electricity consumption in 2020, compared to just 8 percent in 2010 (Chart 1).
What percentage of electricity comes from renewable sources in 2020? Renewable energy accounted for nearly 20 percent of U.S. utility-scale electricity generation in 2020, with the majority coming from hydropower (7.3 percent) and wind power (8.4 percent). Solar power generation (including distributed power generation), which accounted for 3.3 percent of total US power generation in 2020, is the fastest growing power source.
Which state uses the most renewable energy 2020?
These are the states that, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration produce the most renewable energy (millions of megawatt hours):
- Texas (33.95)
- Washington (01/25)
- California (19.52)
- Iowa (13:30)
- Oregon (13.11)
- Oklahoma (10:50)
- New York (9.38)
- Kansas (8.27)
Who uses the most renewable energy in the US?
Vermont generates a whopping 99.9 percent of its electricity from renewable sources. In terms of total renewable electricity generation, the national leaders are California (97 million MWh), Texas (91 million MWh), and Washington (74 million MWh).
Which state uses most renewable energy?
Washington is the number one state for renewable energy with a total installed capacity of 23,884 gigawatts (GW). Hydropower provides more than two-thirds of the state’s total capacity and consumption, while wind is becoming an increasingly important contributor to the grid, accounting for 7.5 percent of total capacity.
What is the largest renewable energy source in 2020?
Wind, currently the most prevalent source of renewable electricity in the United States, grew 14% in 2020 compared to 2019. Utility-scale solar generation (from projects larger than 1 megawatt) increased 26%, and small solar systems, such as . Connected rooftop solar panels up 19%.
Where does Texas get its electricity 2021?
Generation, demand and capacity. Early power plants produced electricity primarily from coal, steam, or hydropower. Today, Texas still generates electricity from some of these traditional sources, but increasingly relies on natural gas and renewable resources, primarily wind.
How much electricity does Texas generate?
Texas produces about 429.8 TWh of electrical energy.
Who supplies electricity in Texas?
There are five electric utilities in Texas: Oncor, CenterPoint, AEP Texas North, AEP Texas Central, and TNMP.
Where does ercot get its energy?
An analysis of data from ERCOT (the Texas grid operator) by Joshua D. Rhodes shows where Texas gets its energy from. The highest share came from natural gas at 46 percent in 2020, while wind accounted for almost a quarter at 23 percent, up quite a bit from 8 percent a decade ago.
How much of Texas power is coal?
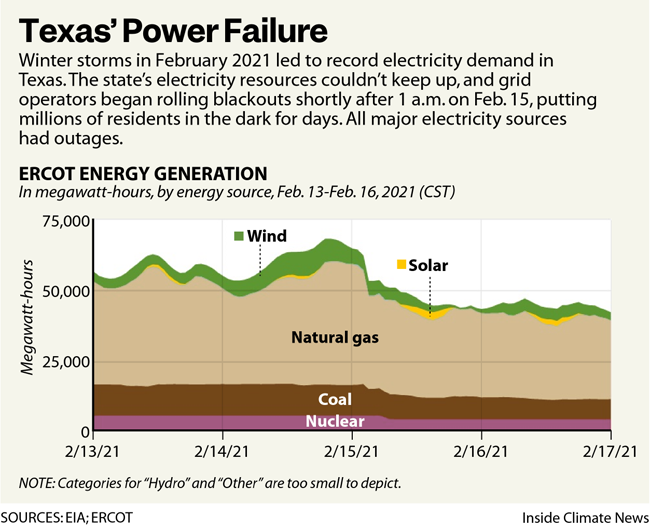
In 2019, Texas had a total summer capacity of 125,117 MW across all of its power plants and net generation of 483,201 GWh. The corresponding power generation mix consisted of 53.5% natural gas, 19.0% coal, 17.3% wind, 8.6% nuclear, 0.9% solar, 0.3% hydro, 0.3% biomass and 0.1% % other sources.
How much electricity in Texas comes from nuclear power? Nuclear power accounts for less than 5% of Texas’ total electric capacity but produces nearly 10% of the state’s electricity, third behind natural gas and coal. The Lone Star State exports about 2% of the electricity it generates. There are two operating nuclear power plants in Texas.
How many coal power plants are in Texas?
Electric power plants: 340 (3% total in US) Coal plants: 20 (2% total in US) Petroleum plants: 17 (1% total in US) Natural gas plants: 162 (5% total in US) Nuclear plants: 2 (2% total US) Hydropower: 25 (1% total US) Other Renewables: 114 (4% total US)
What is the largest power plant in Texas?
The WA Parish Generating Station is a 3.65-gigawatt (3,653 MW) twin-fired power plant located near Thompsons, Texas.
Where are coal plants in Texas?
| Surname | location | Year of construction open |
|---|---|---|
| Coleto Creek | fannin | 1980 |
| Fayette | La Grange in Fayette County | 1979 (615MW) 1980 (615MW) 1988 (460MW) |
| Harrington | Potter County | 1976 (360MW) 1978 (360MW) 1980 (360MW) |
| JK Spruce | Bexar County | 1992 (566MW) 2010 (878MW) |
How many coal burning power plants are there in Texas?
Texas has 40 coal-fired generators at 20 locations with a combined capacity of 21,240 megawatts (MW). At the bottom of this page is a map of the coal fired power plants in Texas.
What energy does Texas use the most?
Texas uses more natural gas and most other energy sources. How Much Natural Gas Does Texas Use? Data shows Texas consumes approximately 3,992.2 trillion BTUs of natural gas.
What uses the most power in Texas?
The US-EIA also analyzed how Texas’ energy consumption breaks down by sector.
- Industrial = 52.7% (7,499.3 trillion BTU)
- Transportation = 23.4% (3,324.4 trillion BTU)
- Housing = 12.4% (1,767.3 trillion BTU)
- Housing = 11.4% (1,626.7 trillion BTU)
Who supplies energy in Texas?
There are five electric utilities in Texas: Oncor, CenterPoint, AEP Texas North, AEP Texas Central, and TNMP.
What percentage of US energy comes from Texas?
Texas produces more electricity than any other state and generates almost twice as much as second-place Florida. In 2021, Texas accounted for about 12% of the nation’s total net electricity generation.
How much coal does Texas have?
Texas has an estimated 9 billion tons of recoverable coal reserves, nearly 4% of the country’s total reserves. The state is the second largest brown coal producer in the United States, after North Dakota, and the ninth largest coal producer overall.
What percentage of Texas electricity is coal?
Electricity Generation: 429.8 TWh (11% US total) Coal: 44,200 MSTN (4% US total) Natural Gas: 7,480 Bcf (30% US total) Crude Oil: 725,800 Mbarrel (31% US total) Ethanol: 8,100 Mbarrel (3% total US)
How many coal plants are in Texas?
Existing Coal Power Plants Texas has 40 coal-fired generators at 20 locations with a combined capacity of 21,240 megawatts (MW). At the bottom of this page is a map of the coal fired power plants in Texas.
What percentage of US energy comes from Texas?
Texas produces more electricity than any other state and generates almost twice as much as second-place Florida. In 2021, Texas accounted for about 12% of the nation’s total net electricity generation.

