The following is an article contributed by George Sakellaris, President and CEO of Ameresco.
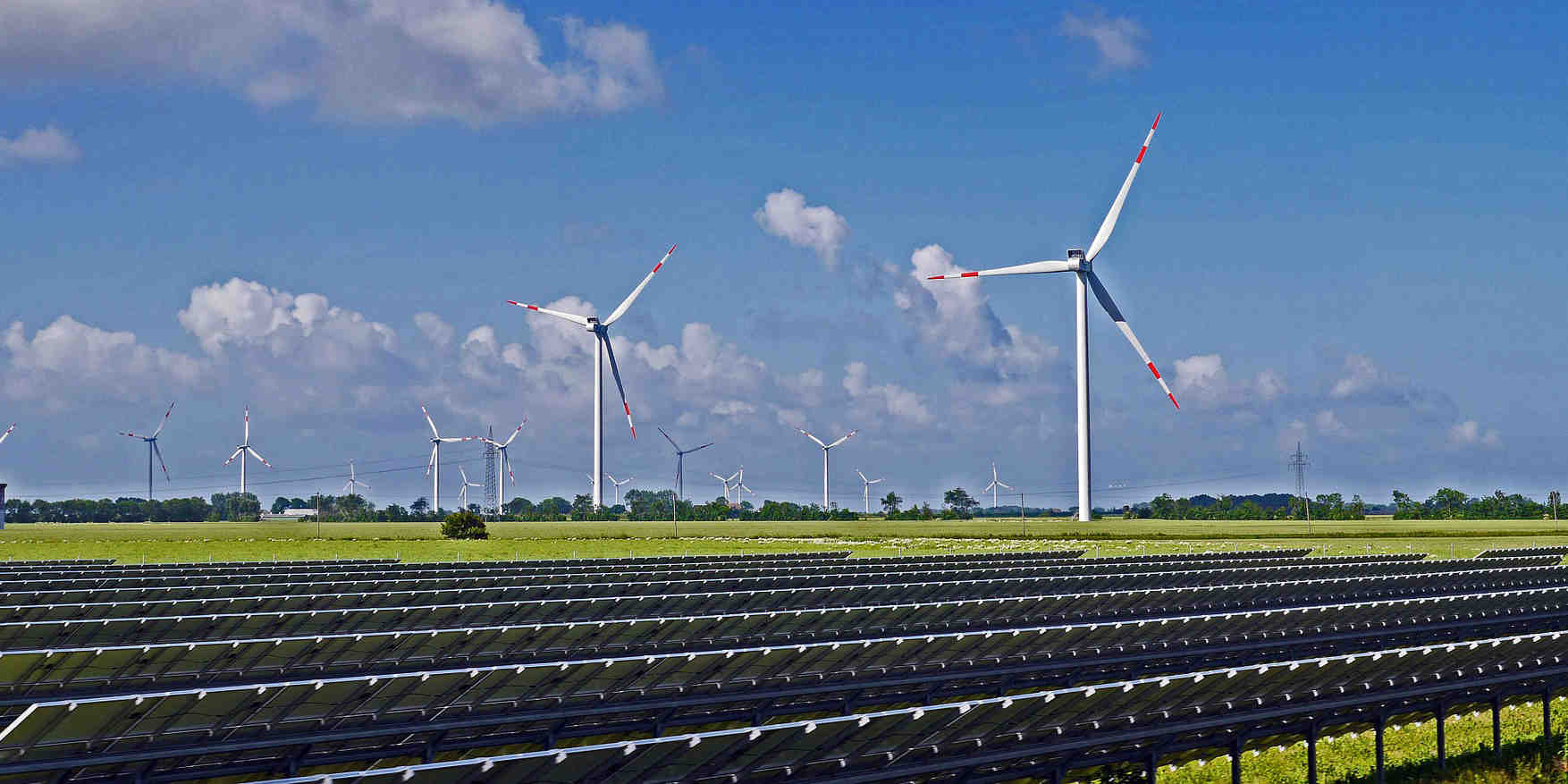
In a world that continues to grapple with the effects of climate change and a global energy crisis that shows no signs of slowing down, it has never been clearer that the time to innovate our national approach to energy development is now. For too long, US federal policy has taken a siled perspective and focused almost exclusively on the development of popular intermittent renewable solutions, such as wind and solar – and that’s not enough.
Think about it this way: What happens when a Category 6 hurricane hits an offshore wind farm? Those turbines are down and the security of the grid is threatened, potentially enough to leave millions without access to electricity for a period of time.
To make substantial progress in the energy transition, it is critical that we embrace a holistic and diversified approach to the adoption of clean energy that encourages the development of permanent renewable solutions, or those that do not rely solely on intermittent power. Renewable farms allow us to reliably respond to energy demand regardless of varying weather conditions, which can pose problems for solutions such as wind and solar. The mass adoption of solutions such as hydroelectric power, which uses the natural flow of moving water to generate electricity, or biogas, which takes raw materials such as municipal waste and wood and turns them into energy, would allow us to continue scaling the clean energy transition in one way. significant way.
In June 2022, the Biden administration reinforced the federal government’s long-standing siled point of view and doubled down on intermittent renewables by announcing a two-year pause in imposing new solar energy tariffs. The move is significant, as it signals continued federal support for the adoption of clean energy and encourages the renewal of America’s aging infrastructure, which is highly beneficial. Unfortunately, it doesn’t do much in the way of encouraging the adoption of a more diverse portfolio of sustainable solutions that will more comprehensively strengthen our nation’s energy security.
To understand the context behind the US laser focus on intermittent renewables, I think it is important to examine US energy policy from the early 2000s. At the time, concerns about the impending climate crisis began to gain steam in national conversations. In an attempt to accelerate clean energy deployment and combat growing concerns, the federal government signed the Energy Policy Act of 2005 into law and introduced the Solar Investment Tax Credit.
For that time, the legislation was revolutionary. Those who owned or implemented a solar energy system would receive a tax credit, which was equivalent to 30% of the eligible cost of the system. The ITC has encouraged the mass adoption of solar energy on a commercial and residential scale, as it is quickly becoming much easier, and more importantly cheaper, to adopt clean energy solutions than ever before. If the goal was to familiarize the general public with the benefits of renewable solutions, while simultaneously promulgating the widespread acceptance and implementation of these emerging technologies, the approach worked.
In 2008, total US solar power capacity was only 0.34 GW. Today, that capacity has grown to an estimated 97.2 GW. To put that into perspective, that last figure is enough to power the equivalent of 18 million average American homes.
Diversifying renewable energy solutions

While any move towards accelerating the adoption of clean energy solutions over fossil fuels is a step in the right direction, it is important to take a step back and think strategically about our point of view so that we do not become overly dependent on a single solution. As a good financial advisor will tell you, over-reliance on a single investment, no matter its track record, puts your portfolio at risk. On the same subject : Solar heroes san diego. The same goes for renewable energy solutions.
Although intermittent renewables are often proposed due to their ease of implementation, smaller size and wide distribution compared to centralized plants, fluctuations in weather patterns can impact their reliability if they are not supported well off the grid. Enterprise renewables do not face this same problem because they are not dependent on uncontrolled, external forces.
However, this is not to say that renewable companies do not face their own problems. Like most energy sources, there are trade-offs for production and use. For example, biogas, while it is an excellent method of decarbonizing existing waste, also contains impurities after the refining and compression process. It also faces the obstacle of the urban scale because the large-scale production of the energy form is based on an abundant supply of waste manure or crop materials, which are more easily available in rural agricultural land. In the same lens, hydroelectric power has faced its own set of obstacles as some dams that allow its operation have disrupted the natural patterns of fish migration, and water supply problems in the nation threaten the feasibility of using it as a reliable form of energy.
Despite these obstacles, the benefits of each technology far outweigh the associated drawbacks. For biogas, the end product significantly reduces methane emissions and makes use of excess waste in a highly efficient and clean way. With hydroelectric power, the addition of fish “scales” can mitigate any disruptions to migration patterns and the proper selection of locations for hydroelectric power plants can negate any concerns around water supply.
No form of energy, clean or otherwise, is without its drawbacks. This is why we need to embrace an integrated mix of solutions if we are ever to stand a chance against climate change. But renewable farms allow us to deal with the intermittency of solutions such as wind and solar, reinforcing the existing energy supply.
They are similar to energy storage systems, which are often proposed as a solution to intermittent renewables because they capture excess energy for use at a later date, as they reduce imbalances between energy demand and the production. But like solar and wind energy, energy storage systems are also susceptible to security challenges when their energy reserves are depleted for extended periods of time.
At the end of the day, steady renewables allow us to substantially enhance our national energy security without jeopardizing the reliability of our energy supply. This is especially relevant given the recent Supreme Court ruling, which limits the ability of the Environmental Protection Agency to regulate global warming emissions from the nation’s power plants. Those with the power to effect concrete change, such as corporations, need to take action now.
The dominance of fossil fuels is declining, and as we transition to more efficient solutions, we must ensure that we do so strategically and comprehensively. Wind and solar power are not enough.
We are at a crucial moment in history. There is no doubt that to address the unfolding climate crisis, we need to embrace firm solutions at an accelerated pace. We cannot afford to continue on our current path.
Solar panels fight global warming by producing electricity that prevents us from burning fossil fuels that produce greenhouse gases. They also shade the Earth from the sun.
What is the safest energy source?
Nuclear power is by far the safest source of energy. To see also : What are the 4 main types of solar energy ?. It has more than 330 times less deaths than coal; 250 times less than oil; and 38 times less gas.
What is the cleanest source of energy? Nuclear is a clean energy source with no emissions. It generates power through fission, which is the process of splitting uranium atoms to produce energy. The heat released from fission is used to create steam that spins a turbine to generate electricity without the harmful byproducts emitted by fossil fuels.
What is the best source of energy?
Nuclear power is the most reliable source of energy and it’s not even close | Department of Energy.
What is the number 1 energy source?
Energy Sources in the United States Petroleum (crude oils and natural gas plant liquids): 28% Coal: 17.8% Renewable energy: 12.7% Nuclear electricity: 9.6%”
What are the three best energy sources?
The key insight is that they are all much, much safer than fossil fuels. Nuclear power, for example, results in 99.9% fewer deaths than brown coal; 99.8% less carbon; 99.7% less oil; and 97.6% less gas. Wind and sun are also safe.
What are the top 5 energy sources?
Top 5 Energy Sources in the United States | Natural Gas | petroleum | coal | Nuclear | Renewable.
What is the safest and cheapest source of energy?
The safest sources of energy are also the cleanest: renewables and nuclear. But despite the progress, there is a very long way to go. About 60% of the world’s energy comes from coal and oil; another 25% comes from gas. In fact, only 15% of global energy production is low carbon (renewable or nuclear).
What is the cheapest source of energy?
The report follows the conclusion of the International Energy Agency (IEA) in its World Energy Outlook 2020 that solar energy is now the cheapest electricity in history. The technology is cheaper than coal and gas in most major countries, the prospect finds.
What are the safest source of energy?
Nuclear power, for example, results in 99.9% fewer deaths than brown coal; 99.8% less carbon; 99.7% less oil; and 97.6% less gas. Wind and sun are also safe.
Which energy source is least harmful to the environment?
Harnessing wind power is one of the cleanest and most sustainable ways to generate electricity because it produces no toxic pollution or global warming emissions. Wind is also abundant, inexhaustible and affordable, making it a viable, large-scale alternative to fossil fuels.
What is the safest energy source for the environment?
Nuclear power, for example, results in 99.9% fewer deaths than brown coal; 99.8% less carbon; 99.7% less oil; and 97.6% less gas. Wind and sun are also safe.
Which form of energy has the least pollutants?
Solar energy leads to the least environmental pollution in the process of exploitation and utilization because it does not emit harmful gases into the environment.
Are wind and solar energy worth the effort?

Sunlight and wind are inherently unreliable and dilutive in energy. As such, adding solar panels and wind turbines to the grid in large quantities increases the cost of generating electricity, locks in fossil fuels, and increases the environmental footprint of energy production.
Is wind and solar energy cost effective? When it comes to the cost of energy from new power plants, onshore wind and solar are now the cheapest sources – they cost less than gas, geothermal, coal or nuclear. Solar, in particular, has fallen at a breakneck pace.
What are the problems with wind and solar energy?
Solar and wind also pose problems for the environment. Wind especially, but also the sun, require absurdly large tracts of land, disrupt animal habitats, kill hundreds of thousands of birds and bats, and destroy natural landscapes. The extraction of materials for these technologies has scarred lands in the world.
What are the negatives of wind and solar energy?
The cost of wind energy has fallen by 85% in the last 20 years….
- Intermittent: Solar energy – while abundant – is not constant. …
- Energy storage: One solution to the challenge of intermittent energy sources is to invest in energy storage. …
- Cost: It is very expensive to bring a solar plant online.
What are the problems with solar energy sources?
The cons are that it produces energy only when the sun shines, it needs a significant amount of land, and that some solar technologies require rare materials.
What are the problems with wind energy?
As with all energy supply options, wind energy can have adverse environmental impacts, including the potential to reduce, fragment or degrade habitat for wildlife, fish and plants. Additionally, rotating turbine blades can pose a threat to flying wildlife such as birds and bats.
Does solar or wind energy have the best potential?
Wind is a more efficient energy source than solar. Wind turbines release less CO2 into the atmosphere. A wind turbine produces 4.64 grams of CO2/1kWh while the solar panel produces 70 grams of CO2/1kWh. Wind energy consumes less energy and produces more energy compared to solar panels.
Which renewable energy has the greatest potential?
Solar energy has the greatest potential among all renewable energy sources.
Which is best solar energy or wind energy?
The enormous amount of energy generated with solar energy is much more than that of wind. If we talk in terms of maintenance, solar panels are better than wind turbines. Solar panels work effectively for up to 30 years and require much less maintenance.
Why is solar energy better than wind energy?
Unlike wind turbines, solar panels have no moving parts that could cause more wear and tear, resulting in higher maintenance costs after the initial investment. When comparing solar versus wind farms, based on the numbers above, solar energy comes out ahead as a cheaper way to generate energy for residential use.
What is the most effective energy source?

Nuclear power is the most reliable source of energy and it’s not even close. Nuclear power is America’s workhorse. For six decades, it has been putting itself back on its feet to provide steady, reliable, carbon-free power to millions of Americans.
What is the best source of energy and why? Nuclear power, for example, results in 99.9% fewer deaths than brown coal; 99.8% less carbon; 99.7% less oil; and 97.6% less gas. Wind and sun are also safe.
What is the #1 energy source?
Energy Sources in the United States Petroleum (crude oils and natural gas plant liquids): 28% Coal: 17.8% Renewable energy: 12.7% Nuclear electricity: 9.6%”
What are the top 5 energy sources?
Top 5 Energy Sources in the United States | Natural Gas | petroleum | coal | Nuclear | Renewable.
What is the most popular energy source?
Oil â 39% Accounting for about 39% of global energy consumption, oil has historically been the most used energy source in the world. Despite a decline over the past two decades, oil demand has remained high mainly due to demand from emerging economies, particularly non-OECD countries.
What is the number 1 most used energy source in the world?
Oil is the most consumed primary energy fuel in the world. In 2021, approximately 184.2 exajoules of oil were consumed. This represents an increase of almost six percent compared to the previous year.
Is solar or wind energy better for the environment?

Wind is a more efficient energy source than solar. Compared to solar panels, wind turbines release less CO2 into the atmosphere, consume less energy and produce more energy overall. In fact, one wind turbine can generate the same amount of electricity per kWh as approximately 48,704 solar panels.
Is solar power better than wind power? The most efficient solar panels can capture and convert about 23% of the sun into energy. Not bad, but wind turbines turn about 50% of the captured wind into energy. Looking at those basic measurements, wind power appears to be more than twice as efficient as solar power.
Is solar and wind energy bad for the environment?
Every type of energy comes with some cost to the environment, and solar and wind energy is no different. Bats and birds are killed every year by wind turbines. Solar panels can occupy large tracts of wilderness formerly used by a host of wildlife, from pronghorns and turtles to coyotes and rattlesnakes.
Which is better for the environment wind or solar?
Wind is a more efficient energy source than solar. Wind turbines release less CO2 into the atmosphere. A wind turbine produces 4.64 grams of CO2/1kWh while the solar panel produces 70 grams of CO2/1kWh. Wind energy consumes less energy and produces more energy compared to solar panels.
What is a major disadvantage of solar and wind energy?
The major disadvantage is its low reliability, since the wind varies over time. It is also not a high density energy source. Therefore, it needs a relatively high installation cost. It also requires some form of storage and regulation.
Is wind energy good or bad for the environment?
As with all energy supply options, wind energy can have adverse environmental impacts, including the potential to reduce, fragment or degrade habitat for wildlife, fish and plants. Additionally, rotating turbine blades can pose a threat to flying wildlife such as birds and bats.
Why is solar energy better then wind energy?
Unlike wind turbines, solar panels have no moving parts that could cause more wear and tear, resulting in higher maintenance costs after the initial investment. When comparing solar versus wind farms, based on the numbers above, solar energy comes out ahead as a cheaper way to generate energy for residential use.
What is the difference between solar energy and wind energy?
| Wind energy | solar energy |
|---|---|
| Wind turbines are used to convert wind energy into electrical energy. | Solar panels are used to convert solar energy into electricity. |
Why is solar energy the best energy source?
The sun provides more than enough energy to meet the energy needs of the entire world, and unlike fossil fuels, it will not run out anytime soon. As a renewable energy source, the only limitation of solar energy is our ability to turn it into electricity efficiently and cost-effectively.
What is cheaper solar or wind?
Unsubsidized wind ranges from $28 to $54 per megawatt-hour (MWh), and utility-unsubsidized solar ranges from $32 to $42/MWh. Factoring in subsidies, wind prices fell to $11–$45/MWh and utility-scale solar prices remained relatively stable at $31–$40/MWh.
What is the cheapest energy to produce?
And there is good news for the planet: solar and wind energy, at the scale that a large utility would distribute them, are now the cheapest form of power. They are slightly less expensive than natural gas power plants and much cheaper than coal and nuclear.


