The five main uses of solar energy are solar electricity, solar water heating, solar heating, solar ventilation and solar lighting. There are more uses for solar energy, but homes and businesses typically use solar energy for these purposes.
What is solar energy made of?
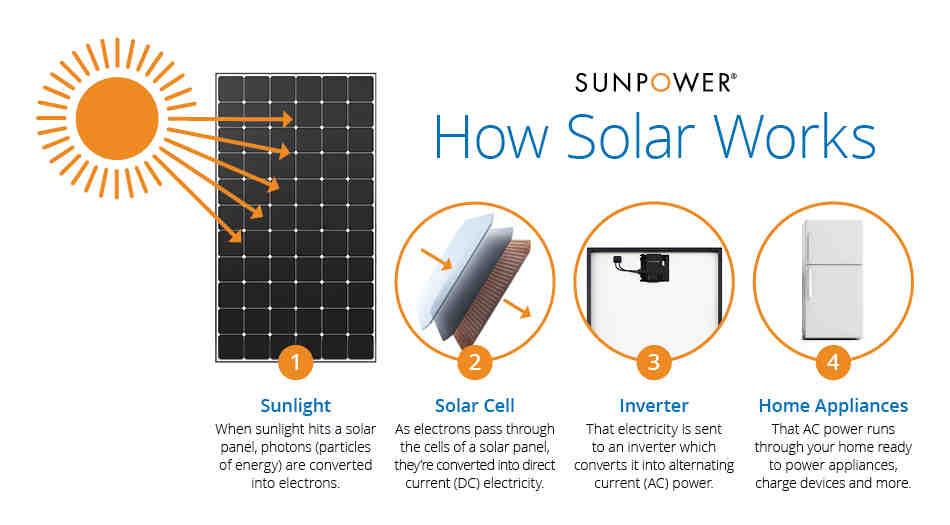
Solar energy is any type of energy generated by the sun. Solar energy is created by nuclear fusion that takes place in the sun. This may interest you : Utilities reverse pressure against the growth of solar panels on the roof. Fusion occurs when protons from hydrogen atoms violently collide in the sun’s nucleus and fuse to create a helium atom.
What materials make solar panels? What are solar panels made of?
- Silicon solar cells. …
- Metal frame (typically aluminum) …
- Glass sheet. …
- Standard 12V wire. …
- Bus wire. …
- Make the solar cells. …
- Solder the solar cells to create a panel. …
- Install a back sheet, a front glass layer, and a frame.
What is solar energy in simple words?
The answer is simple: solar energy. Solar energy is simply the light and heat that comes from the sun. This may interest you : Renewable energy, new perspectives for photovoltaic cells. People can harness the sun’s energy in a few different ways: Photovoltaic cells, which convert sunlight into electricity. Solar thermal technology, where the sun’s heat is used to make hot water or steam.
What is solar energy short answer?
The answer is simple: solar energy. Solar energy is simply the light and heat that comes from the sun. People can harness the sun’s energy in a few different ways: Photovoltaic cells, which convert sunlight into electricity.
What is solar energy explain for kids?
Solar energy is energy generated directly from sunlight. Solar energy can be used for thermal energy or converted to electrical energy. Renewable energy. When we use solar energy, we don’t use any of the Earth’s resources like coal or oil. This makes solar energy a renewable energy source.
What is solar power and examples?
By definition, solar energy is energy derived from the sun. The energy can be used directly to heat and light homes, or it can be converted into electricity using solar energy technologies such as solar panels.
How is solar made into energy?
Solar technologies convert sunlight into electrical energy through photovoltaic (PV) panels or through mirrors that concentrate solar radiation. This energy can be used to generate electricity or be stored in batteries or thermal storage.
What do solar panels do simple explanation?
Simply put, a solar panel works by allowing photons, or particles of light, to release electrons from atoms, generating a flow of electricity, according to the University of Minnesota Duluth (opens in new tab).
How long do solar panels last for?
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic or photovoltaic panels, are made to last over 25 years. In fact, many solar panels installed since the 1980s are still operating at expected capacity. Not only are solar panels remarkably reliable, but solar panel longevity has dramatically increased over the past 20 years.
What is solar material?
Solar cells are made of silicon balls. These are polycrystalline structures that have the atomic structure of a single crystal. The most commonly used method for creating the boule is known as the Czochralski method. During this process, a silicon seed crystal is dipped in molten polycrystalline silicon.
What is solar System material?
Silicon. Silicon is by far the most common semiconductor material used in solar cells, accounting for approximately 95% of modules sold today.
What is the raw material for solar panels?
The basic raw material of a solar panel is pure silicon. However, the outer structure that surrounds an array of solar cells in each solar panel is made of glass. The glass must be highly transparent to allow sunlight to penetrate the frame.
How much solar energy hits the Earth?

Solar energy is the most abundant energy resource on Earth – 173,000 terawatts of solar energy reach the Earth continuously. That’s over 10,000 times the world’s total energy use.
How much solar energy hits Earth every second? Globally, throughout the year, the Earth system – land surfaces, oceans and atmosphere – absorbs an average of about 240 watts of solar energy per square meter (one watt is one joule of energy every second).
How much solar energy hits the Earth per hour?
In a single hour, the amount of energy from the sun that hits the Earth is more than the entire world consumes in a year. To put this in numbers, from the US Department of Energy: Every hour, 430 quintillion Joules of energy from the sun hit the Earth.
How much of the Sun’s energy is hitting the Earth?
In total, approximately 70% of the incident radiation is absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere and surface, while about 30% is reflected back into space and does not heat the surface. The Earth radiates energy at much longer wavelengths than the Sun because it is cooler.
How much solar energy hits the Earth per day?
6. Solar energy is the most abundant energy resource on Earth – 173,000 terawatts of solar energy reach the Earth continuously. That’s over 10,000 times the world’s total energy use. 5.
How much energy does solar produce per hour?
How much energy do solar panels produce per hour? The average solar panel produces 170 to 350 watts every hour, depending on the region and weather conditions. This works out to about 0.17 kWh to 0.35 kWh per solar panel.
How much solar energy hits the Earth per year?
The 70% of the solar energy that the Earth absorbs per year is equivalent to approximately 3.85 million exajoules. In other words, the amount of solar energy that hits the Earth in an hour is more than enough to power the world for a year.
How much solar energy hits the Earth each day?
6. Solar energy is the most abundant energy resource on Earth – 173,000 terawatts of solar energy reach the Earth continuously. That’s over 10,000 times the world’s total energy use.
How much solar energy hits the Earth in percentage?
Thus, about 71% of the total solar energy received is absorbed by the Earth system. Of the 340 watts per square meter of solar energy that falls on Earth, 29% is reflected back into space, mostly by clouds, but also by other shiny surfaces and the atmosphere itself.
How much solar energy does the Earth receive?
Earth’s climate is a solar-powered system. Globally, throughout the year, the Earth system – land surfaces, oceans and atmosphere – absorbs an average of about 240 watts of solar energy per square meter (one watt is one joule of energy every second).
Can solar power the world?
With countries racing to end their dependence on the fossil fuels that cause climate change, it is a time for expansion into renewable energy. Now, an international team of researchers has determined that if all available roofs were equipped with solar panels, they could generate enough electricity to power the world.
How many solar panels could power the world? “How many solar panels could power the world? 23 billion solar panels. That’s what we’re going to need.” (Of course, the world will never be 100% solar powered. Other sources, such as wind and hydropower, have a big role to play.
What would happen if the whole world went solar?
If, for example, we produced all the world’s annual electricity with solar panels, CO2 emissions could be reduced to less than 1 billion tons. It would be a difference of 22 billion tons of carbon dioxide that would not have to pollute the air or cause global warming.
How many solar panels would it take to power the whole world?
How many solar panels would it take to power the world? It would take 51.4 billion 350W solar panels to power the world! Put another way, this is the equivalent of a solar power plant covering 115,625 square miles.
What would happen if the world ran on renewable energy?
After that, it is possible to feed the planet entirely with sustainable energy. Switching to wind, water and solar power worldwide could eliminate 4-7 million deaths from air pollution annually, while first slowing and then reversing the effects of global warming and, in doing so, would stabilize the global energy sector.
Can the world run on solar power?
With technological improvements, it would be possible in the near future to send solar energy anywhere on the globe, even without the help of batteries. For example, a grid that encircles the globe could easily do this. Based on Bloomberg NEF forecasts, solar and wind power will power half of the globe by 2050.
How much solar power is needed to run the world?
How many solar panels would it take to power the world? It would take 51.4 billion 350W solar panels to power the world! Put another way, this is the equivalent of a solar power plant covering 115,625 square miles.
Can the world run on renewable energy?
If the world turned away from fossil fuels, could we generate the energy needed to power the world with 100% renewable energy? According to a new report from LUT University in Finland and the Energy Watch Group, a German non-profit organization, the answer is yes.
How important is solar energy to us?
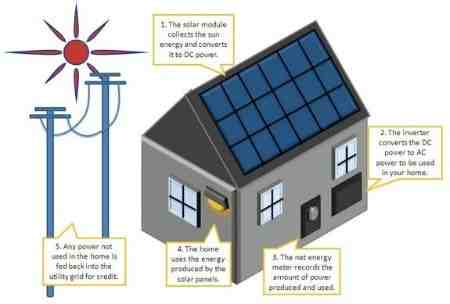
The sun is a free, sustainable and clean resource that we can harness in place of conventional electricity to power our lives. Solar energy can be used to provide heat, light and other electricity-dependent needs in homes and buildings.
How important is solar energy? Solar energy is energy derived from sunlight. Whether you realize it or not, the sun already powers our planet, providing the energy we need to keep our environment and our population growing. The amount of sunlight that reaches the Earth’s atmosphere is enough to supply all of our needs, and then some.
Why is solar power important to our future?
Solar energy creates pure, clean and renewable energy from the sun, a perfect alternative to fossil fuels such as natural gas and coal. It also reduces the carbon footprint and greenhouse gases worldwide.
Why is solar so important?
The importance of solar energy is, first of all, to be clean, renewable and, with the latest technologies available, to be able to supply a much more significant proportion of our energy needs. Currently, solar energy production represents about 1% of global electricity generation.
Why is solar energy important to life on Earth?
It radiates light and heat, or solar energy, which makes life on Earth possible. Plants need sunlight to grow. Animals, including humans, need plants for food and the oxygen they produce. Without the heat of the sun, the Earth would freeze.
Why is solar energy important to life on Earth?
It radiates light and heat, or solar energy, which makes life on Earth possible. Plants need sunlight to grow. Animals, including humans, need plants for food and the oxygen they produce. Without the heat of the sun, the Earth would freeze.
Why is solar energy important to us?
The sun provides more than enough energy to meet the world’s energy needs, and unlike fossil fuels, it’s not going to run out anytime soon. As a renewable energy source, the only limitation on solar energy is our ability to turn it into electricity efficiently and cost-effectively.
What is solar energy and why is it important to life on the earth?
Solar energy is constantly flowing away from the sun and throughout the solar system. Solar energy heats the Earth, causes wind and weather, and sustains plant and animal life. Energy, heat and light from the sun flow in the form of electromagnetic radiation (EMR).
How important is solar energy to us essay?
Solar energy is very important as it is a clean and renewable energy source. So that means it won’t damage the land in any way. In addition, it is available daily. Likewise, it does not cause any kind of pollution.
How important is solar energy to us?
The sun provides more than enough energy to meet the world’s energy needs, and unlike fossil fuels, it’s not going to run out anytime soon. As a renewable energy source, the only limitation on solar energy is our ability to turn it into electricity efficiently and cost-effectively.
What is solar energy and why is it important to life on the earth?
Solar energy is constantly flowing away from the sun and throughout the solar system. Solar energy heats the Earth, causes wind and weather, and sustains plant and animal life. Energy, heat and light from the sun flow in the form of electromagnetic radiation (EMR).



