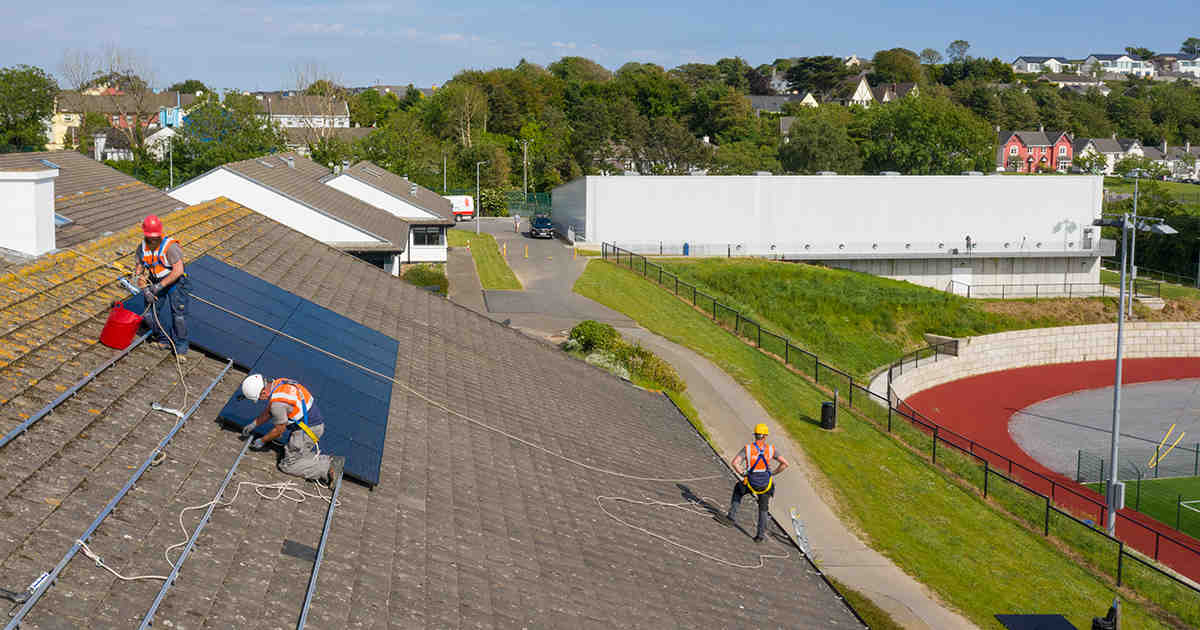
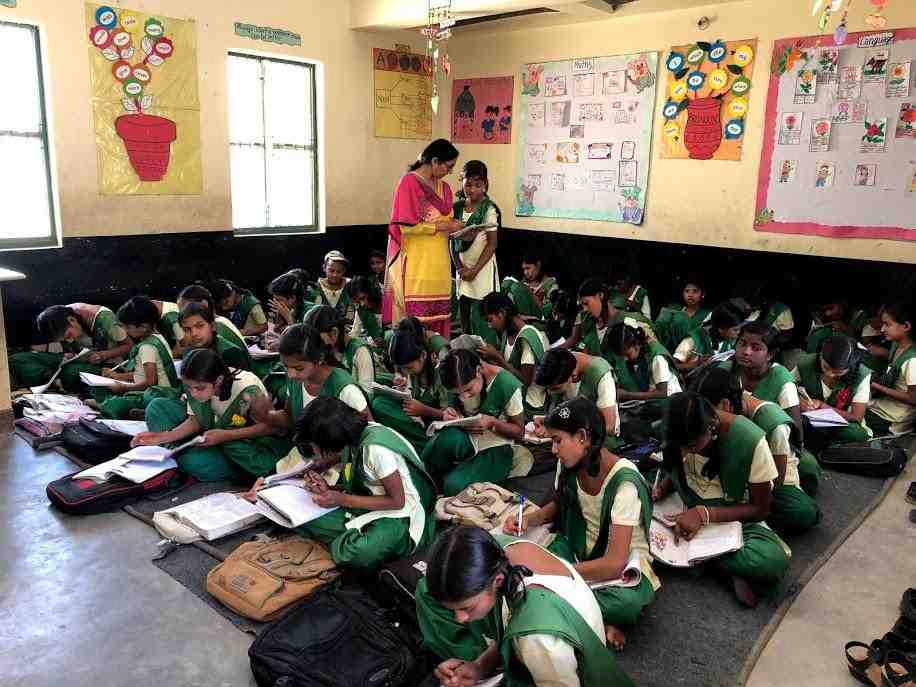
Going to the bank in his hometown in western India used to be a slow, frustrating process for Kiran Patil, as frequent power outages — sometimes lasting for days — turned what should have been a quick errand into a protracted ordeal.
The 59-year-old farmer often had to stand in line for hours at
, his local branch in Aitawade Budruk village, or abandon the transaction and return the next day, wasting the time he should have spent growing his crops.
That all changed after the building was fitted with a set of solar panels and back-up batteries in 2018, breaching the bank’s
and gives it a steady supply of clean electricity.
“The transactions now are so smooth and fast,” Patil told the Thomson Reuters Foundation. “These days we even find time for a quick chat with the branch manager over a cup of tea to learn about the latest services and facilities.”
A more reliable banking experience also brings in new customers who previously did not have time for long waiting times or who were worried about never knowing when they would be able to access their money.
Since the solar power system was installed at RBL in Aitawade Budruk, the bank has opened 25 to 30 new accounts every month – 10 times more than before, said branch manager Sandeep Banne.
As India ramps up its use of renewable energy in a bid to wean itself off climate-warming coal, the country is leaning heavily on solar power to cut carbon emissions and help stabilize a grid strained by coal shortages and rising demand from a population trying to keep cool in warmer weather summers.
But some communities have discovered another benefit of the solar push: greater access to the financial system for millions of the country’s unbanked, including the estimated 20% of Indian adults who don’t have access to a bank account or formal line of credit.
Raghuraman Chandrasekaran, founder and managing director of E-Hands Energy, the Chennai-based firm that set up the solar plant in Aitawade Budruk, said his company has installed such systems in more than 920 rural banks across India, helping to bring more than 6 million people into the formal banking system.
The company plans to install units at up to 100 more rural branches before the end of the year, he said.
“Residents in rural areas walked or spent their precious money to transport themselves from the villages to the nearest bank branch, waiting (there) for hours… simply because the bank had no power all day and the computers could not function,” Chandrasekaran said .
MODERN BANK
The three kilowatt solar power system at the Aitawade Budruk branch – which powers everything from fans and lights to computers and alarm systems – means the bank now has reliable power about 95% of the time, said Banne, the branch manager.
On cloudy days, backup batteries take over, he said.
has so far equipped more than 2,000 banks in rural India with solar energy, estimates Shyam Kumar Garg, who resigned as deputy chairman of the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development last October.
The systems feed into India’s drive to install 500 gigawatts (GW) of renewable energy capacity by 2030, up from around 115 GW now, more than half of which is solar.
E-Hands Energy’s chief operating officer Kakumanu Prathap Sagar said the solar systems the company has installed at banks around India help cut around 3,000 tonnes of carbon emissions every year.
Using solar energy can also cut costs, said Banne at the RBL in Aitawade Budruk, noting that the department now spends a fraction of what it used to spend on grid power and diesel for its back-up generators.
The solar systems cost between 130,000 and 150,000 Indian rupees ($1,650 to $1,900) to install and maintain for four years, and pay for themselves in about four years, he added.
For villagers, the biggest benefit is finally being able to use public services they never had access to before, said Pratibha Budruk, head of Aitawade Budruk’s village council.
As the bank suffered power outages and frequent losses of internet connection, payments of pensions, student grants, loans and insurance were often delayed, putting a strain on people who relied on the money, Budruk said.
“The transition of rural banks to solar power … has opened the doors of modern banking facilities to our local villagers,” she said.
SOLAR POWER CHALLENGES
In a country where 65% of the population lives in rural areas, according to the World Bank, switching land banks to solar energy could even slow the migration of young people from villages to cities as more economic opportunities at home emerge, an energy management expert said. Binoy Krishna Choudhury.
“Solarization of banks is a good step to develop the rural economy,” said Choudhury, who teaches at the Indian Institute of Social Welfare and Business Management in Kolkata.
But projects to bring solar panels to rural banks face a number of obstacles, said Russell deLucia, director and founder of the Small-Scale Sustainable Infrastructure Development Fund, a US-based nonprofit.
Potential hurdles include finding ways to transport and install the equipment at far-off, often off-road locations, said deLucia, whose company helps E-Hands raise financing for its solar projects.
Once the systems are up and running, finding skilled technicians nearby to fix anything that goes wrong is another problem, he said.
Despite these challenges, Budruk, head of the village council, wants more banks to harness solar energy as a way to both improve the lives of rural communities and limit worsening climate change such as extreme heat.
“Installing solar systems in the banks is like planting trees throughout the year to clean the air we breathe,” she said.
“When the whole world is trying hard to slow global warming and the effects of climate change, this is a small contribution from our village.”
In which two markets are green bonds growing the most?

This article is from the Thomson Reuters Foundation, the charitable arm of Thomson Reuters See the article : A safer, less expensive and fast charging aqueous battery.
Green finance is increasing the level of financial flows (from banking, microcredit, insurance and investments) from the public, private and non-profit sectors to sustainable development priorities.
Who are the biggest buyers of green bonds?
More videos on YouTube All regions saw an increase in the amount raised from green bonds, with Asia Pacific up 30 percent year-on-year for a market share of 22 percent. Europe’s dominance of green bonds is driven by France, which accounts for 13. This may interest you : Homing in on longer-lasting perovskite solar cells.4 percent of the global total, making it the most active issuing nation.
Which countries top the green bond market?
Where is the market for green bonds most developed? China maintained its role as the largest issuer of green bonds among EMDEs, issuing $59 billion in 2021, or 63 percent of the total. Non-financial corporate issuers in China took over financial institutions for the first time.
How big is the green bond market?
After bonds from Nigeria, Chile and China, plans from Saudi Arabia and Kenya to finance the transition to greener industry are good examples of the change. France remains the world’s largest sovereign issuer of green bonds, with over $40 billion of green debt outstanding.
Who are the buyers of green bonds?
In 2021, green bond issuance in the United States amounted to US$81.9 billion, while China came in second with green bonds worth US$68.1 billion.
What is the green bond market?
The global green bond market was valued at USD 433.30 billion in the year 2021. Green bonds are used to finance green projects such as renewable energy, clean transportation and long-term water management.
How large is the green bond market?
Buyers of green bonds are typically institutional investors, often with either an ESG mandate (environment, social and governance) or an environmental focus. Other buyers include investment managers, governments and corporate investors.
What are green bonds examples?
Green bonds were created to finance projects that have positive environmental and/or climate benefits. The majority of the green bonds that are issued are green “use of proceeds” or asset-linked bonds. The income from these bonds is earmarked for green projects, but is covered by the issuer’s entire balance sheet.
Are green bonds a good investment?
A continued acceleration of green issuance drove the green bond market to just over half a trillion (US$517.4 billion) in 2021, according to Climate Bonds Market Intelligence. [i] The year is the highest since the inception of the market and maintains the trend of 10 consecutive years of green market expansion.
Which country has largest green bond market?
Green bonds can finance various projects, most often related to renewable energy (eg wind, solar, water), recycling and clean transport. More specifically, examples of projects financed with green bonds are: Renewable energy. Energy efficiency.
How big is the green bond market?
We believe that green bonds are a “no-brainer” for customers with a focus on sustainable investment. Green bonds offer similar returns, ratings and return profiles to other fixed income investments, and they finance projects that have a concrete and measurable effect in the work to meet environmental challenges.
Who is the largest issuer of green bonds?
| In 2021, green bond issuance in the United States amounted to US$81.9 billion, while China came in second with green bonds worth US$68.1 billion. | The global green bond market was valued at USD 433.30 billion in the year 2021. Green bonds are used to finance green projects such as renewable energy, clean transportation and long-term water management. |
|---|---|
| Characteristic | Green bonds in millions of US dollars |
What is the rank of India in emerging green bond market?
–
What are the benefits of green loans?

–
India has emerged as the sixth largest country in the Asia-Pacific region in terms of the total amount of green bonds issued in 2021. Green bond issuance from India increased 523% from a year ago to $6.8 billion during the year, showed a Knight Frank report.
What is a green loan facility?
Environmental benefits An increase in green loans is expected to increase private funds for green projects, and contribute to a significant reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and prevention of deterioration of natural capital. An increase in green loans and green deposits will increase individual awareness of green loans.
How does a green loan work?
What qualifies for a green loan? A green home improvement loan is for anyone planning to make improvements to their home to increase energy efficiency. It can be for large retrofitting projects that may include solar panels and insulation, but also for smaller works – such as installing new windows or doors or having a new boiler installed.
What is the difference between a green loan and a sustainability linked loan?
What is a green loan? A green loan is similar to a green bond in that it raises capital for green qualified projects. However, a green loan is based on a loan that is typically smaller than a bond and is made in a private business.
How does a green loan work?
Green lending in mortgages Lenders offer green mortgages to borrowers on projects that have been built or renovated with environmental factors in mind. Green mortgage borrowers get a 1% discount on the mortgage interest rate for existing homes and up to a 1.25% discount for new builds.
What is the benefit of a green loan?
Unlike green loans as discussed above, the use of the proceeds is not the distinguishing feature. A sustainability linked loan encourages a borrower to improve their sustainability profile over the term of the loan. Borrowers receive a reduced margin for achieving pre-agreed ESG-related KPIs. Confirmation.
Can you pay off plain green loans early?
Green lending in mortgages Lenders offer green mortgages to borrowers on projects that have been built or renovated with environmental factors in mind. Green mortgage borrowers get a 1% discount on the mortgage interest rate for existing homes and up to a 1.25% discount for new builds.
What is a green loan?
Lender’s benefits Green loans can provide a stable cash flow, unless borrowers default on the loan. Lenders can show that they actively invest in green loans, support green projects and thus gain a positive opinion.
Why are lenders Green?
With a regular green loan, you can apply today and have cash in your account already tomorrow. Can I afford to repay this loan in full? You repay your Plain Green loan in installments – from 10 months to 26 months. There are no penalties or additional fees for repaying the loan early.
What makes a green loan?
Green loans are loans intended for sustainable, environmentally friendly purposes, such as reducing CO2 emissions, or purposes that contribute to the green transition in society, such as developing new environmentally friendly technology.
What is the benefit of a green loan?
Which green lending products can the banks offer? Green mortgages give homeowners a discount on the mortgage interest if the house meets certain energy standards. Sustainability-related loans or revolving credit facilities provide borrowers with discounted interest rates for achieving ESG goals or benchmarks.
Why is credit Green?
Green loans are loans intended for sustainable, environmentally friendly purposes, such as reducing CO2 emissions, or purposes that contribute to the green transition in society, such as developing new environmentally friendly technology.
What is green finance Wikipedia?

Lender’s benefits Green loans can provide a stable cash flow, unless borrowers default on the loan. Lenders can show that they actively invest in green loans, support green projects and thus gain a positive opinion.
Green credit has a significant negative impact on carbon emission intensity at a significant level of 1%. Every 1% increase in green credit reduces the intensity of carbon emissions by 0.441%, indicating that green credit has the potential to reduce carbon emissions.
What is sustainable finance group?
Sustainable finance or green finance is the set of financial regulations, standards, norms and products that pursue an environmental goal, and in particular to facilitate the energy transition.
What is sustainable finance examples?
What does sustainability mean in finance? Sustainable finance refers to the process of taking environmental, social and governance (ESG) into account when investment decisions are made in the financial sector, leading to more long-term investments in sustainable economic activities and projects.
What is the meaning of sustainable finance?
The Oxford Sustainable Finance Group is a world-leading center focused on aligning finance with global environmental sustainability.
What is the role of finance in sustainability?
Some examples of sustainable finance include green loans or green bonds, self-financing of renewable energy, carbon credits, public institutional equity investments and much more.
What is sustainable finance examples?
Sustainable Finance is the process of taking due account of environmental, social and governance (ESG) considerations when investment decisions are made in the financial sector, leading to increased long-term investment in sustainable economic activities and projects (European Commission).
What is the difference between green and sustainable finance?
Finance teams are an asset to your organization and an important element in building a sustainable world. To live up to this potential, they must recognize the risks and opportunities associated with sustainability and be able to act on them. Without this, the finance function can be a barrier to change.
What are the three main elements of financial sustainability?
Some examples of sustainable finance include green loans or green bonds, self-financing of renewable energy, carbon credits, public institutional equity investments and much more.
What is an example of financial sustainability?
Climate finance provides means to deal with climate adaptation and mitigation, green finance has a broader scope as it also covers other environmental goals (e.g. biodiversity protection/restoration), while sustainable finance extends its domain to environmental, social and governance factors (ESG ).
How does durability affect investment?
Sustainability is often represented schematically. The figure at the top of this page suggests that there are three pillars of sustainability – economic viability, environmental protection and social justice.
How do you define durability?
You can raise money through donations, grants, user fees or all of the above, to name a few examples. But that is not the whole story. A financial sustainability plan will also include other types of resources you can acquire, such as in-kind support, voluntary staff or shared resources from other organisations.
What is durability used for?
We show that more durable assets require larger down payments, which makes them more difficult to finance, because durability affects the price of assets and thus the total financing requirement more than their security value.
What does strong durability mean?
Durability is when something lasts a long time. The durability of your favorite hiking boots means that they will not wear out even after you have walked many miles in them. Use the noun durability to describe the quality of duration or strength that keeps something working or holding it together.
How big is the green bond market?

What is durability used for? Durability is the ability to last a long time without significant deterioration. A durable material helps the environment by saving resources and reducing waste and the environmental impact of repair and replacement.
Something durable is strong and lasts a long time without breaking or becoming weaker. Bone china is strong and durable. Synonyms: durable, strong, tough, sound More Synonyms for durable. durability (djÊÉrÉbɪlɪti , US dÊr- ) uncountable noun. Airlines recommend hard-sided bags for durability.
How much is the green bond market worth?
| The global green bond market was valued at USD 433.30 billion in the year 2021. Green bonds are used to finance green projects such as renewable energy, clean transportation and long-term water management. | How many green bonds were there in 2021? At a glance 2021: Sustainability Bonds 2 billion in 2021, a 23% increase from the USD 162.5 billion observed in 2020. In 2021, Climate Bonds captured 287 issuer names, an increase of 184% compared to 2020. |
|---|---|
| Characteristic | Value in billions of US dollars |
Which country has the most green bonds?
–