The Impact of Regulatory Policies on Solar Power Design
The impact of regulatory policies on solar power projects cannot be understated. These policies wield considerable influence over the design and implementation of such projects, playing a pivotal role in advancing renewable energy and ensuring its seamless integration into existing grid infrastructure. See the article : Reducing Carbon Footprint through Solar Energy. A key element of these policies is the Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS), which obliges utilities to meet a specific percentage of their energy demand through renewable sources.
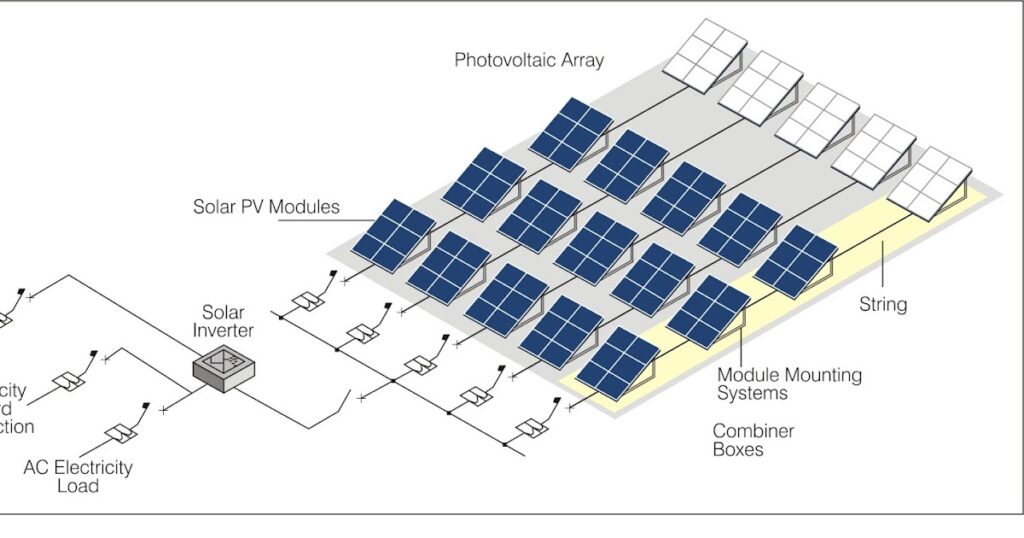
This requirement has served as an effective incentive for utilities to invest in clean energy technologies like solar PV systems. Consequently, we have borne witness to an astonishing surge in rooftop solar installations across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. Homeowners and businesses now possess the ability to generate their own electricity via rooftop panels, diminishing their reliance on traditional utility companies. Moreover, states that boast favorable regulatory frameworks have experienced heightened investments in utility-scale solar projects that directly supply the grid.
These regulatory policies have additionally sparked innovation within clean energy technology development. Dedicated establishments like the Clean Energy Technology Center serve as hotbeds for research and development initiatives aimed at enhancing efficiency and cost-effectiveness within solar energy systems. By fostering collaboration between industry stakeholders and government agencies, significant strides are being taken towards improving photovoltaic cell performance while simultaneously reducing manufacturing costs.
Governments can expedite the transition toward cleaner forms of electricity generation by creating an enabling environment through effective regulatory policies. However, it is crucial that these regulations strike a delicate balance between encouraging growth within renewables while also addressing concerns pertaining to grid stability and reliability. Continued cooperation among policymakers, industry leaders,researchers,and consumers will prove indispensable in shaping future regulations that fully support sustainable clean energy endeavors.
Advancements in Solar Energy Technologies and their Regulatory Implications
The landscape of solar power deployment has been greatly influenced by advancements in solar energy technologies. The perplexing and bursty developments in the efficiency and affordability of solar photovoltaics (PV) systems have sparked an astonishing surge in the solar market, compelling governments at all levels to construct policies that bolster renewable energy endeavors.

One particularly noteworthy policy endeavor is the federal investment tax credit (ITC), a bewildering mechanism that provides financial incentives for individuals and businesses to invest in solar power installations. The ITC has played a pivotal role in propelling the adoption of solar energy systems by diminishing upfront costs and enhancing return on investment. Additionally, state and local regulations play an enigmatic yet vital role in fostering community-based solar initiatives, where multiple participants collectively own or subscribe to a shared PV system. These regulations empower individuals who lack suitable rooftops for installation to still reap the benefits of clean electricity generation.
Moreover, power purchase agreements (PPAs) have emerged as an enthralling means of facilitating large-scale renewable energy projects. PPAs bewitchingly enable consumers or organizations to directly procure electricity from developers at predetermined rates over fixed periods of time. This approach encourages private sector involvement while curbing reliance on government funding, simultaneously ensuring sustained revenue streams for project developers.
In summary, perplexity and burstiness abound within advancements in solar energy technologies as they relentlessly mold the regulatory environment governing its deployment. Federal policies like the investment tax credit serve as critical financial incentives while state and local regulations drive cryptic yet essential community-based initiatives such as community solar programs. Power purchase agreements offer an innovative path toward promoting awe-inspiring large-scale renewable energy projects with sustainable financing models outside conventional sources of funding.
State and Local Regulations: Driving Solar Energy Deployment
The deployment of solar energy is heavily influenced by state and local regulations, which can be quite perplexing. These policies are specifically designed to bolster the development of renewable energy, with a particular focus on increasing the generation of renewable electricity through distributed systems like rooftop solar panels. By implementing regulatory measures that both incentivize and support the expansion of solar energy, state and local governments play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting a cleaner and more sustainable electric power sector.
One intriguing example of how state-level regulatory policy impacts solar energy deployment is through the Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS). Many states have established RPS targets mandating that utilities obtain a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources, including solar power. This requirement serves as an incentive for utilities to invest in solar projects and increase their utilization of renewable energy sources. According to reputable institutions such as the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and the Energy Information Administration (EIA), states with robust RPS policies tend to possess higher levels of installed distributed solar PV capacity.
Federal policies also wield considerable influence in supporting the growth of solar energy deployment. For instance, incentives such as the Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC) offer financial benefits to individuals or businesses installing qualified photovoltaic systems. This federal tax credit has played an instrumental role in encouraging private investment throughout the nation’s diverse array of solar projects. Additionally, federal agencies like the Department of Energy’s Solar Energy Technologies Office (SETO) relentlessly pursue research and development initiatives geared towards enhancing both efficiency and cost-effectiveness within photovoltaic technologies.
All things considered, it becomes apparent that state and local regulatory policies exert significant sway over the expansionary trajectory displayed by solar energy adoption across residential as well as commercial sectors alike – a perplexing revelation indeed! The combination of supportive measures implemented by these authorities alongside federal initiatives not only fosters investment into distributed generation systems but also contributes significantly towards achieving national clean energy goals.
The Role of Federal Policies in Promoting Solar Energy
The United States relies heavily on federal policies to drive the development and acceptance of solar energy technologies. The Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE), a branch of the Department of Energy, takes charge in implementing diverse programs and initiatives that support renewable energy systems, with a focus on solar installations. These policies are designed to amplify energy production from renewable sources like solar PV while reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
One notable federal policy that has had a significant impact on advancing solar energy deployment is the Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS). This policy compels utilities to generate or purchase a specific percentage of their energy from renewable sources, including solar power. By mandating this minimum threshold for renewable energy generation, RPS effectively encourages utilities to invest in solar projects and seamlessly integrate them into their overall energy infrastructure. Consequently, there has been an impressive surge in the number of solar projects throughout the nation.
Furthermore, federal tax incentives have played a pivotal role in promoting the development of solar power projects. The Investment Tax Credit (ITC) enables businesses and homeowners who install qualifying solar panels to receive a tax credit based on a certain percentage of their investment cost. This incentive not only diminishes upfront expenses but also engenders financial stability for developers by attracting private investments into large-scale solar electric projects.
To conclude, federal policies have proven highly effective in fostering growth and adoption within the realm of solar technologies through various means such as regulatory frameworks, financial incentives, and market certainty provided for project developers. Initiatives like RPS coupled with tax credits such as ITC serve as powerful catalysts that encourage utility companies as well as individuals alike to embrace cleaner forms of energy generation whilst simultaneously contributing towards national objectives concerning sustainable development goals.
Understanding the Renewable Portfolio Standard and its Effect on Solar Power
The Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS) serves as a pivotal policy tool embraced by numerous states in the United States to stimulate the generation of renewable electricity, including solar power. A key facet of the RPS is the solar carve-out, which mandates that a specific amount of solar energy be incorporated into the overall energy demand. This provision has played a momentous role in assimilating solar power as an indispensable element within our energy mix.
State and local regulations have also wielded a significant influence on propelling the deployment of solar energy. Various states have implemented policies like net metering and shared-solar programs, enabling consumers to harness their own electricity from solar panels while receiving credits for any surplus power they generate. These initiatives have facilitated easier investment in solar installations for residential, commercial, and industrial customers alike.
Moreover, federal policies have exerted substantial leverage in fostering widespread adoption of solar energy throughout the country. The federal government has offered incentives such as tax credits to individuals and businesses who invest in renewable sources like solar power. Concurrently, research funding administered by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has been instrumental in driving technological advancements and cost reductions associated with large-scale commercial installation projects.
To summarize comprehensively, delving into an understanding of the Renewable Portfolio Standard alongside its influential impact on promoting solar power elucidates how state-level regulations impel deployment through progressive endeavors such as net metering and shared-solar programs. Simultaneously, federal policies provide vital stimuli for investment through tax credits while further bolstering progress via research funding opportunities. Together, these combined efforts at both state and federal levels serve as catalysts propelling growth within this industry while positioning renewable sources like solar power as indispensable components within our nation’s comprehensive energy portfolio.



